Abstract
The article discusses one of the young types of tourism - gastronomic. According to the World Tourism Organization (UNWTO), gastronomic tourism in recent years has been ranked 3rd among other types of tourism. In 2019, the volume of the world market of gastronomic tourism amounted to more than $ 45 billion. Every third tourist considers the national cuisine as an important tourist motive that encourages them to go on a trip. The national cuisine of France, Italy, Spain, Austria, Germany is popular all over the world, which is why the listed countries are recognized leaders in gastro-tourism. The national cuisine of China, India, Thailand, Mexico attracts attention with its exoticism. Every year the demand for gastronomic tours is becoming higher, the audience of consumers is expanding, in connection with which there is a variety of types of gastronomic tours. The article presents the characteristics of the most popular types of gastronomic tours, classified according to the territorial feature and the purpose of the trip. For Russia, gastronomic tourism is still a new phenomenon, but it is actively developing. The author of the article considers the concept of "gastronomic tourism", as well as formulates the features that characterize this type of tourism and lists the factors influencing the active development of gastronomic tourism in Russia. The author paid special attention to the geography of gastro-tourism in Russia. The analysis of various materials allowed the author to identify the problems that hinder the development of gastro-tourism in Russia.
Keywords: Gastronomic tourism, gastronomic tour, national cuisine, regions of Russia, tourism
Introduction
Until recently, tourism has developed dynamically around the world. According to UNWTO statistics, the number of international trips grew from year to year. Traveling to different countries of the world, people got acquainted with the culture and life of other peoples. In the preamble to the "Global Code of Ethics for Tourists" (UNWTO General Assembly, 01.10.1999, Santiago, Chile), UNWTO members stated their conviction that tourism, through direct contact of representatives of different cultures and lifestyles, contributes to ensuring friendship and mutual understanding between the peoples of the world.
Against the backdrop of events related to the COVID-19 pandemic and the closure of borders, Russian tourists are redirecting their eyes to the domestic market and looking for new travel routes in Russia. Tourism in the dock period in Russia and around the world was characterized by an increasingly widespread diversification of the sector and the growth of domestic tourism.
Table 1 lists the groups of factors influencing the development of tourism in the region.
There is no doubt that tourism will recover its positions, and existing trends, including the search for new ways to meet the growing tourist demand, will continue to determine the development of the industry. Currently, each region of the Russian Federation is looking for new opportunities and resources to attract tourists to itself and is trying to offer something unique. A similar unique offer is gastronomic tourism. This type of tourism is characterized by the following features:
Resources and objects of gastronomic tourism for the development of an appropriate tourist offer are present in every country;
Non-mass;
All-season;
Interaction with various types of tourism: cultural, educational, event, ecological, rural;
The ability to combine elements of various gastronomic tours in one program;
The main purpose of the trip as part of gastronomic tourism is to get acquainted with the national cuisine.
Problem Statement
The development of gastronomic tourism in the Russian Federation is hampered by a number of problems:
Insufficient number of gastro-tourism facilities in the regions;
High tariffs for transportation services on the territory of the country;
Discrepancy between the price of the services provided and the quality of service;
Lack of promotion in the domestic and international tourist market;
Lack of incentives for enterprises in the regions that produce local food products;
Lack of qualified personnel;
Lack of a single information bank of data on gastronomic tourism and the corresponding tourist offer.
Research Questions
In course of the study the following questions were raised:
What is the importance of developing gastronomic tourism?
Why is the popularity of gastronomic tourism growing in the modern world?
What features are characteristic of gastronomic tourism in Russia?
Purpose of the Study
Supposedly, the answers to the above questions will help to achieve the goal and will contribute to increasing the popularity of gastronomic tourism both in the Russian Federation and around the world.
Research Methods
In this article, general scientific theoretical research methods were used:
- Analysis of literature on the development of gastronomic tourism in the world and in Russia;
- Systematization of theoretical data on the term "gastronomic tourism";
- Generalization of statistical data of tourist flows in the framework of gastronomic tourism;
- Synthesis that unites the positions of tourism specialists in relation to the considered type of tourism.
Literature Review
Gastro tourism is one of the relatively new, but already popular types of tourism around the world. However, the term "gastronomic tourism" was not originally used. In 1998, L. Long, Associate Professor of the Department of Folk Culture at Bowling Green University, Ohio (USA), expressed the idea of the possibility of acquainting people with the culture of the regions through local cuisine. From that moment on, all trips aimed at acquaintance with the cuisine of a country or region began to be referred to as “culinary tourism”.
For several years, scientists from around the world have studied culinary tourism. The world's first article on the topic of culinary tourism was written in 2001 by the American economist Eric Wolff, and after he devoted an entire book to this topic. And these are not all the achievements of the scientist, in 2003 he founded The International Culinary Tourism Association. In 2012, the association was renamed The World Food Travel Association (2022). At the same time, the term "gastronomic tourism" came into use, replacing "culinary tourism". In 2015, UNWTO singled out gastronomic tourism as a separate type of tourism, in connection with which it received an official status.
Analysis of various sources made it possible to identify the most common formulations of the term "gastronomic tourism":
Tourism, when tourists and visitors planning to taste some or all of the cuisine of a certain area or to carry out activities related to gastronomy visit certain destinations (Dracheva & Hristov, 2015);
Travel in order to get acquainted with the peculiarities of the national cuisine of the country, production and preparation of products and dishes (Ivanov, 2018);
Travelling across countries and continents to get acquainted with the peculiarities of local cuisine, culinary traditions, in order to taste dishes or products that are unique for a visiting person (Borovkova et al., 2016);
Type of tourism associated with familiarization, production, cooking technology and tasting of national dishes and drinks, as well as culinary traditions of the peoples of the world, which aims to obtain a unique unforgettable experience (Generalova, 2018);
A trip, the main purpose of which is to get acquainted with the peculiarities of the national cuisine, the peculiarities of production and the technology of food preparation, to improve professional skills (Kulkova, 2017);
Travel to regions rich in gastronomic resources, recreation and entertainment, including: visits to primary or secondary food producers, food festivals, fairs, events, culinary demonstrations, food tastings or any other food-related events (Cheglazova & Grigoryan, 2020);
A journey in which regions rich in gastronomic resources can create recreational experiences or entertainment, the goals of which are: visits to primary or secondary producers of gastronomic products, gastronomic festivals, fairs, events, culinary demonstrations, food tastings food or any related activities to food (Bajkadamova & Shajsultanova, 2020);
A special type of tourism, the purpose of which is to get to know a particular country through the peculiarities of the national cuisine, which is attractive for something special and unique (Kireeva & Chernikh, 2021);
A trip to taste the place to feel its soul (World Food Travel Association, 2022);
Seeking and enjoying unique and unforgettable food and drink experiences, both away from home and nearby (Official site of the Russian Gastronomic Tourism Association, 2022).
The difficulty in defining the term is due to the close relationship of gastro-tourism with other types. But at the same time, this relationship allows you to cover various segments of the tourist market, activate tourist flows and offer the consumer (tourist) interesting tour programs.
The importance of the development of gastro-tourism in certain regions of the country is considered in their works by domestic scientists, such as Basyuk, Kuklina, Vishnevskaya, Salamatina, Alexandrova, Stelmakh.
An analysis of special literature, as well as publications in scientific journals, showed that foreign authors are also studying this topic. Such authors as Jesús ClaudioPérez Gálvez, Miguel Jesús Medina-Viruel, Francisco González Santa Cruz are engaged in the study of terminology in the field of gastrotourism, the history of its formation and development, as well as the study of the prospects of this direction (Cruz et al., 2020), Gálvez et al. (2017), professor of cultural economics at the University of Cordoba, considers gastronomy to be one of the main keys in making a tourist destination attractive.
A number of scientific works of the following foreign authors are devoted to the content of gastronomic tourism, analysis of objects included in the "gastronomic tours": Shenoy, Chaney, Ryan, Hull, Mitchell.
Discussion
In Russia, gastronomic tourism is a new and rapidly developing area. This was influenced by the following factors:
- The growing popularity of a healthy lifestyle.
- The growing popularity of cooking shows and programs.
- Popularization in social networks (Vkontakte, Instagram) of aesthetic photographs with dishes of national cuisine.
- An increase in the cost of food during the rest. Food during the trip accounts for 30% of the total costs. According to the results of a sociological survey conducted by the Momondo service in 2019, more than half of the respondents (52%) are ready to spend more on food while traveling than in ordinary life.
- An increase in the number of tourists wishing to visit fashionable or unusual food outlets in the region or city. For example, the Moscow food mall “Depo. Moscow ", located in the center of the capital on the territory of the former trolleybus depot. This site is positioned as the largest food mall in Europe and Russia and presents 75 gastronomic concepts on an area of 3.5 hectares. According to the results of a sociological survey conducted by the Momondo service in 2019, 83% of respondents find information about such establishments and sites on the Internet.
- Search for new taste sensations, tastings of certain, in some cases expensive or exotic dishes. According to the results of a sociological survey conducted by the Momondo service in 2019, 42% of respondents, when choosing a vacation spot and planning a route, take into account the peculiarities of the local cuisine.
Increasing interest in the production process of food and beverages specific to a particular region. The main consumers of gastronomic tours are:
Tourists who like to eat deliciously, but are not ready to give up other components of the rest: swimming at the sea, excursions, entertainment;
Chefs and food service owners travelling to gain practical experience in the field of culinary, professional development and the conclusion of direct contracts for the supply of food and beverages;
Gourmets who enjoy not the process of preparing a particular dish, but its absorption, evaluate the taste of the dish both as a whole and separately for each ingredient, pay special attention to the taste combinations of products;
Individual tourists travelling on their own.
Currently, various tours are presented in the tourist market within the framework of gastronomic tourism. One of the signs of dividing existing gastronomic tours is a territorial feature, and according to it, rural and urban gastronomic tours are distinguished, each of which can be eventful, educational, etc. (Figure 1).
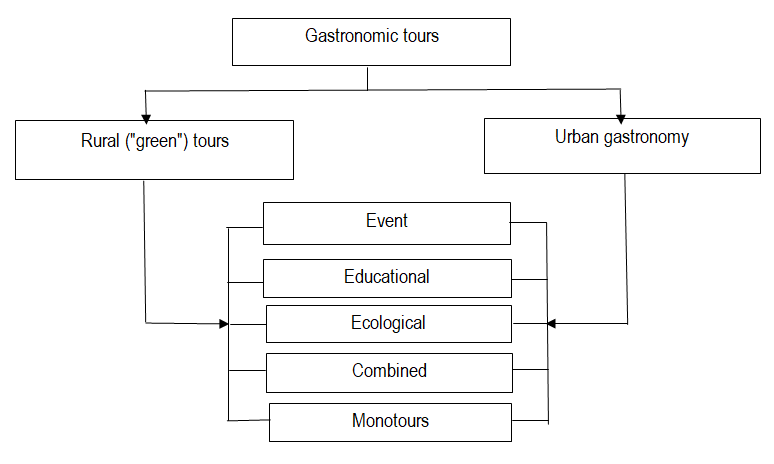
Let's consider the features of each type of gastronomic tour.
Rural ("green") gastronomic tours:
Conducted in rural areas;
Tourists are accommodated in individual or specialized accommodation facilities located in rural areas (alternatively, in small towns without multi-storey buildings);
The food for tourists includes dishes typical for this region and prepared from organic products, also typical for this region;
The tour program includes: picking wild berries in the forest, vegetables and fruits on farms, truffle hunting;
Organizing and conducting thematic excursions within the tour, for example, "On a visit to the farmer".
Urban gastronomy:
Conducted in cities;
The tour program provides for visiting restaurants of national cuisine or enterprises producing this or that local product with obligatory tasting (for example, a factory for the production of confectionery products);
Providing tour participants to conclude a profitable deal for the supply of a particular product to another region (this is a business component of the city gastronomic tour, provided for specially organized groups).
Going on a gastro tour, regardless of the territorial feature, a tourist can pursue various goals, according to which they are distinguished: event-driven, educational, ecological, combined and mono-tours (Table 2).
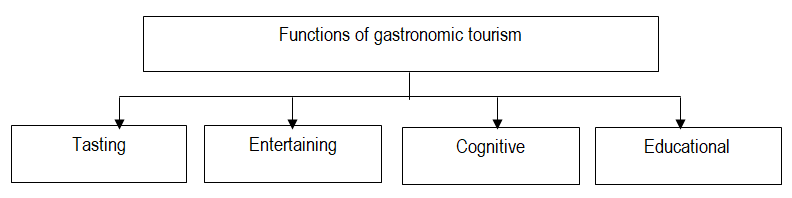
Based on the above classification of gastro tours and their characteristics, it is possible to formulate the functions of gastro tourism (Figure 2).
Representatives of more than 180 nationalities live on the territory of Russia, with customs, culture, and gastronomic traditions characteristic of each of them. All this is the basis for the development of gastro-tourism. For example, the methods of processing the meat of forest animals and game, fish, mushrooms and berries, worked out over the centuries, are the basis for the preparation of various dishes typical for the taiga territories of Russia.
The most popular national cuisines in Russia are Caucasian, Russian, Tatar and Far Eastern.
Caucasian cuisine is a general concept that unites the traditions of Armenian, Azerbaijani, Ossetian, Abkhazian, Chechen and Georgian cuisine. Each of them has its own special dishes. But there are also similar dishes, for example, shashlik - small pieces of meat, previously soaked in marinade, are cooked over charcoal. You can try original Caucasian dishes by going on a gastro tour to Stavropol.
Russian cuisine is one of the most interesting, delicious and hearty cuisines in the whole world. Traditional Russian dishes include cabbage soup, porridge, pies, pancakes, pickles, as well as sbiten, kvass, etc. Religion had a great influence on the formation of the traditions of Russian cuisine; therefore, lean dishes, which have no analogues in the whole world, are its integral part (Kireeva & Kuznetsov, 2018).
Tatar cuisine is characterized by delicious, easy-to-prepare and hearty dishes. Tatars reliably guard the secrets of the national cuisine, passing them on from generation to generation. In Tatar cuisine, great importance is attached to the first courses - broths and soups. One of the most popular of them is shulpa - meat broth flavored with aromatic herbs, as well as shulpa soup.
Far Eastern cuisine combines dishes from Russian settlers, borrowings from Asian neighbors and elements of the cuisine of indigenous peoples. The region's special pride is honey, of which there are more than 10 types of honey. Among them there are also rare species: dandelion, aralia, dimorphan, lespedecia.
Table 3 shows the most popular directions of gastronomic tours in Russia.
The gastronomic tours considered are based on a rich program that corresponds to a gastronomic theme and meets the main purpose of a tourist's trip - acquaintance with the local cuisine of a particular region.
The gastronomic tour programs include thematic excursions with visits to gastromuseums, catering establishments, farms, wineries. In some cases, the program includes a master class on cooking a particular dish under the guidance of an experienced chef. And in some regions of Russia, tourists are encouraged to catch fish with their own hands or go for mushrooms and berries. So, using the example of the Perm Territory, it can be noted that when visiting the Belogorsk St. Nicholas Missionary Monastery, tourists and excursionists have the opportunity to get acquainted with dishes made from wild berries and mushrooms, for the collection of which the monastery organizes special trips of novices throughout the Perm Territory. In the village of Ilyinsky, within the framework of visiting museums (the houses are the property of the Stroganov Counts), tea drinking with local concoctions and using local forest berries is necessarily held. In general, mushrooms belonging to the family are in great demand in the Perm Territory. (milk mushrooms ( Fr. and (Bull., Fr.) Pers.), russula ( Pers.), saffron milk caps ( Gröger), ceps ( Bull.)) Mushroom data collection begins in the second decade of July and ends in October. Among forest berries, the following are in special demand: blueberries ( L.), lingonberries ( L.), cranberries ( Pers.) and cloudberries ( L.). The collection of blueberries and cloudberries takes place in July-August. Gourmets may be interested in the following products: horsetail strobila (Equisetum arvense L.), used as a filling for pies (first half of May); jam from green cones of Scots pine (Pinus sylvestris L.), harvested in late May - early June.
The desire to get acquainted with the local cuisine, try a special dish from the chef, visit a famous restaurant - all this is possible not only during a gastronomic tour (duration more than 24 hours), but also during an excursion (duration less than 24 hours). Table 4 presents the most interesting gastronomic excursions in Russian cities.
Of the excursions listed in Table 3, receptive tour operators make up multi-day service programs.
Findings
Based on the collected and analyzed information, trends in the development of gastro-tourism in Russia are formulated:
- Gastronomic tourism is not a mass type of tourism in the modern Russian tourist market.
- The number of participants in a gastronomic tour, as a rule, is no more than 10-15 people.
- Tourists travel both in organized groups and individually. Tourists often choose organized tours from such Russian tour operators as "Alean", "Dolphin". The most popular among organized tourists are gastronomic tours to Krasnodar, Anapa, Gelendzhik, Crimea, Kaliningrad, Rostov-on-Don and Astrakhan.
- Gastronomic tours in their pure form are most often short-lived - in most cases these are weekend tours, 2-3 days.
- Programs of gastronomic tours are tied either to resort regions, or to regions with famous and interesting attractions. Tourists who come to relax at the sea or see the sights enjoy visiting farms and wineries in the region. In this case, the elements of gastronomic tourism add variety to the tour program. For example, while resting at the resorts of the Black Sea coast, tourists have the opportunity to visit the wineries of Anapa, Abrau-Dyurso, Novorossiysk, Kerch and the Taman Peninsula. As part of cultural and educational tours to Kirzhach, Nizhny Novgorod, Kazan, Yoshkar-Ola, Cheboksary, tourists are offered lunch or dinner from Russian, Tatar and Mari cuisine.
- The cost of gastronomic tours is quite high - on average, it is from 50 thousand rubles per person. In this case, the service of transportation, for example, to the Black Sea coast, the Kaliningrad region or the Far East is paid additionally. Tours within your region or to a neighboring area are much cheaper. For example, one of the most common offers for residents of Moscow and the Moscow region is trips to Tver, Torzhok, Tula, Kostroma, Suzdal, etc. Thus, the cost of a gastro tour depends on the region, time of year and the richness of the program.
- Increase in the number of gastronomic events in the regions.
- Increase in demand for gastronomic tours: according to the Association of Tour Operators of Russia (ATOR), the demand for gastronomic tours annually increases by 17%. In 2020-2021, the increase in demand was significantly influenced by the growth in the popularity of domestic tourism amid a pandemic and closed borders in mass destinations.
- The development of gastronomic tourism is supported at the state level. For example, in 2017, the federal project "Gastronomic Map of Russia" was launched, aimed at promoting regional cuisine. The project is being implemented in 20 regions of the country, bringing together manufacturers, restaurateurs and chefs.
- Formation of a positive image of the region by creating a gastronomic brand.
Conclusion
All figures and tables should be referred in the text and numbered in the order in which they are mentioned.
The conclusions must be precise and show the balance of the investigation/Las conclusiones According to UNWTO, 6 out of 10 tourists in 2020 canceled their planned vacation trip due to COVID-19. Based on the results of various studies, it was revealed that when choosing trips in the very near future, tourists will pay attention to the following points:
- Observance by tourist enterprises during the service of the so-called "hygiene and safety protocols": the use of personal protective equipment, keeping the distance, etc.;
- Possibility of contactless payment for services;
- The ability to receive a number of services without contacting the staff of accommodation facilities, for example, check-in upon arrival;
- The possibility of ordering food in the room.
According to experts, in the very near future gastronomic tourism will become the most demanded type of tourism. This is due to the fact that the organizers of gastronomic tours focus on a small number of participants, catering from organic products, accommodation in small country hotels and providing the opportunity to spend a lot of time in the fresh air.
Russia has enormous potential for the development of gastronomic tourism on its territory. The development of gastro-tourism will help to attract investment to the region, increase the flow of tourists, and in a number of regions - the extension of the tourist season. Thanks to the development of gastro-tourism, the number of jobs for local residents is increasing in Russian regions, the standard of living is increasing, and conditions are being created for environmental protection.
Thus, in the modern conditions of tourism development, as well as the ever-increasing competition in the tourism sector, gastronomic tourism can become a tool for attracting tourists to the region, the basis for the formation of a positive image and a recognizable brand, as well as solving a number of problems.
References
Bajkadamova, A., & Shajsultanova, S. (2020). Gastronomicheskii turizm - novyi trend dlia sovremennogo turizma [Gastronomic tourism - a new trend for modern tourism]. Scientific evolution, 1(1), 156-161. https://www.elibrary.ru/item.asp?id=42936199
Borovkova, A., Isaenko S., & Savelev, I. (2016). Gastronomicheskii turizm [Gastronomic tourism]. New economy and regional science, 1(4), 56-59. https://www.elibrary.ru/item.asp?id=26711641
Cheglazova, M., & Grigoryan, T. (2020). Gastronomicheskii turizm kak trendovoe napravlenie v industrii turizma [Gastronomic tourism as a trend in the tourism industry]. Priority directions and problems of domestic and international tourism development in russia, materials of the IV All-Russian scientific-practical conference with international participation, 283-287. https://www.elibrary.ru/item.asp?id=44198037
Cruz, F. G. S., Moral-Cuadra, S., Tito, J. C., & López-Guzmán, T. (2020). Gastronomic Motivations and Perceived Value Foreign Tourists in the City of Oruro (Bolivia): An Analysis Based on Structural Equations. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 17(10), 3618. DOI:
Dracheva, E., & Hristov, T. (2015). Gastronomicheskii turizm sovremennye tendentsii i perspektivy [Gastronomic tourism: modern trends and prospects]. Russian regions: looking to the future, 2(3), 36-50. https://www.elibrary.ru/item.asp?id=23944249
Gálvez, J. C. P., Granda, M. J., López-Guzmán, T., & Coronel J. R. (2017). Local gastronomy, culture and tourism sustainable cities: The behavior of the American tourist. Sustainable Cities and Society, 32, 604-612. https://www.doi.org/
Generalova, A. (2018). Osobennosti sprosa na gastronomicheskii turizm [Features of demand for gastronomic tourism]. Economic environment, 3(25). 81-85. https://www.elibrary.ru/item.asp?id=35737121
Ivanov, V. (2018). Gastronomicheskii turizm kak populiarnoe napravlenie v turisticheskoi industrii [Gastronomic tourism as a popular direction in the tourism industry]. Physical culture. Sport. Tourism. Engine recreation, 3(2), 105-113. https://www.elibrary.ru/item.asp?id=35559424
Kireeva, Y., & Chernikh K. (2021). Gastronomicheskii turizm kak faktor razvitiia turizma v kaliningradskoi oblasti [Gastronomic tourism as a factor of tourism development in the kaliningrad region]. Modern problems of tourism and service, Collection of articles of scientific reports following the results of the All-Russian Scientific and Practical Conference, 146-151. https://www.elibrary.ru/item.asp?id=46146605
Kireeva, Y., & Kuznetsov N. S. (2018). Traditsii natsionalnoi kukhni kak privlekatelnyi faktor razvitiia turizma [Traditions of national cuisine as an attractive factor of tourism development]. Management and marketing in mass sports and tourism, Materials of the All-Russian conference with international participation of scientific and practical, 225-229. https://www.elibrary.ru/item.asp?id=32793333
Kulkova, Y. (2017). Gastronomicheskii turizm kak odno iz perspektivnykh napravlenii razvitiia turizma [Gastronomic tourism as one of the promising directions of tourism development]. Current problems of physical culture, sports, tourism and recreation, materials of the V All-Russian scientific-practical conference of students and graduate students with international participation, 234-236. https://www.elibrary.ru/item.asp?id=29281224
Official site of the Russian Gastronomic Tourism Association. (2022). Retrieved on 22 November, 2021 from http://xn--80ag3bh.xn--p1ai/
World Food Travel Association. (2022). Retrieved on 22 November, 2021 from https://www.robertagaribaldi.it/wp-content/uploads/2019/07/2019-State-of-the-Food-Travel-Industry_FINAL-compressed.pdf
Copyright information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
About this article
Publication Date
29 August 2022
Article Doi
eBook ISBN
978-1-80296-126-3
Publisher
European Publisher
Volume
127
Print ISBN (optional)
-
Edition Number
1st Edition
Pages
1-496
Subjects
Economics, social trends, sustainability, modern society, behavioural sciences, education
Cite this article as:
Kireeva, Y., Romanov, A., Kalistratova, A., Tatiana, R., & Norov, P. (2022). Modern Trends And The Development of Gastronomic Tourism In The Russian Federation. In I. Kovalev, & A. Voroshilova (Eds.), Economic and Social Trends for Sustainability of Modern Society (ICEST-III 2022), vol 127. European Proceedings of Social and Behavioural Sciences (pp. 86-98). European Publisher. https://doi.org/10.15405/epsbs.2022.08.11

