Abstract
This paper shows the role of marketing in ensuring resource efficiency. It is found that the marketing is one of the methods of saving resources, making them effective in use. The conclusion about the need to use marketing to increase the efficiency of resource management in the organization is justified. It is suggested to use SWOT-analysis as a marketing technique for choosing a particular strategy, significant for the company in the management of resource efficiency. The forecasting of demand allows receiving evidence-based options in tendencies of change, indicators of quality, expenses and other indicators. Therefore, the system of the resource efficiency at an enterprise has to be guided by forecasting the demand and its task. Improved analysis cost methods (such as the factorial analysis, the functional and cost analysis) help to solve a problem of resource efficiency at the stage of design or production improvement. It is proved that application of the concept of social and ethic marketing promotes development of the resource efficiency program in management.
Keywords: Marketingresource efficiencymarketing impact factors on resourcesmarketing toolssocial-ethical marketing
Introduction
Resource efficiency remains a central problem for Russian economy as a whole and the economy of the individual companies and organizations. The efficient use of all resources is an important task for ensuring the economic security of the state and the viability of future generations.
Resources are an important production base, because they form the content of the products and support the production process. Resources are becoming more varied in quantity and quality, but less available, costly with regard to time and labor. At the same time, the loss or replacement of useful resources with useless resources are viewed as losses, i.e. actions which consume resources, but do not create value for the customer (Vumek, & Dzhons, 2005).
Manufactured products meet the needs and demands of society. Therefore, well-being and vitality of society depend on the rational use of material resources, and, ultimately, the effectiveness of the production process. Different methods of the concept of "lean production," offer resource-saving techniques for production systems, but do not justify the methods of efficient use of resources (Convis, 2001; Haque et al., 2012; Miller, 2011; Ohno, 1988; Shah, & Ward, 2003). One of the methods to affect the resources systematically and to ensure efficiency in their management is marketing resource efficiency. The organization that creates value and generates profit combines and uses various resources. Nevertheless, companies may have identical resources, and yet end up with different competitive advantages. The efficient use of resources in an organization starts with managerial decisions concerning what will be sold, to whom, and how we will ensure efficient production of finished goods and services. The answers to these and other questions are given by marketing and its tools.
Marketing environment factors influencing resources
Marketing resource efficiency aims to explore and promote the idea of sustainable use and conservation of resources, both at the enterprise and in its external environment. For this purpose, it is necessary to analyze many factors of marketing environment, which are divided into external and internal.
The external factors may include:
- State regulation of resource;
- Market conditions;
- Scientific and technical progress;
- Economic factors (the economic situation in the country, the state regulation of the economy in general, the state of economic infrastructure, etc.);
- Ecological (environmental pollution, reduction of mineral reserves, etc.);
- Climatic (the influence of temperature and humidity on the consumption of material resources in the construction of buildings and structures, consumption of fuel and energy resources, the need to protect against adverse environmental influences and others);
- Political.
Since the company cannot directly influence the external factors, it must adapt to these conditions in their activities. And this requires marketing and monitoring of the environment and resources of various markets.
Internal factors under the influence of external factors determine the immediate level of resource efficiency at the enterprise.
Internal factors include:
- technical factors (an impact on the reduction of consumption of certain types of material resources per unit of production and improving the quality and performance of products);
- technological factors (focus on the waste reduction and material loss);
- organization factors (aimed at improving the structure and the organization of production in order to increase the efficiency of resource consumption);
- economic factors (contribute to the creation of conditions for the rationalization of resource use at the enterprise). Economic factors are designed to ensure the successful implementation of innovations to improve resource efficiency at the enterprise.
Analysis of factors allows creating a resource-efficient enterprise strategy. The resource-efficient strategy is a long-term quality focused course of action, which allows one to provide the organization with a competitive advantage, to respond flexibly to changes in the environment, and focused on the achievement of the main goals of the organization based on rational allocation of internal resources allowing to achieve maximum efficiency at the lowest cost with the mandatory use of innovative technologies (Andronova, & Chizhevskaya, 2012).
Methods
Marketing is one of the methods which increases the efficiency of resource use and production as a whole, allows making adequate programs of production and sales, more quickly responds to market changes, creates a competitive advantage, thus contributing to the efficient use of resources. Marketing is aimed at meeting the needs and wants through exchange, designed to orient production to produce the necessary consumer products which are in demand on the market. This is achieved through a careful and thorough market research and an active influence on the market, current demand and formation of needs and consumer preferences.
Consequently, marketing helps to achieve the major management objectives of enterprises, such as:
- Timely provision of necessary resources of required quality and quantity by the study of market suppliers;
- Improving the use of resources (an increase in labor productivity, capital productivity, reduced cycle times, providing the rhythm of processes, reduction in the turnover of working capital, the full use of secondary resources, improving the efficiency of investment) by determining the competitive product prices and reducing production costs;
- Improving the competitiveness of the products by examining consumers and competitors in the market and product promotion on the market.
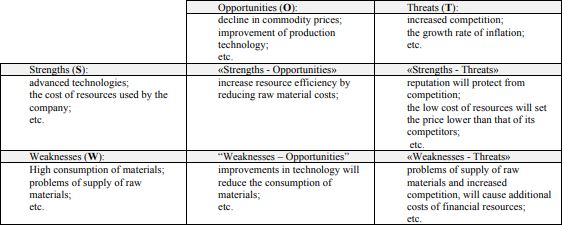
One of the tools in the marketing application in the development of the resource-efficient strategy is SWOT-analysis. The essence of the SWOT-analysis is (Hill, & Jones, 1992; Nikulina, 2015):
•in making efforts to transform weaknesses into strengths and threats into opportunities;
•development of the company's strengths in accordance with its limited possibilities.
Conducting the SWOT-analysis involves a number of stages.
During the first stage the SWOT-analysis strengths - the competitive advantages of the company in various areas - are examined:
•prices of the goods;
•technological advances;
•staff qualifications;
•resource costs;
•the age of fixed assets;
•the geographical location of the enterprise;
•infrastructure;
•the management system, marketing;
•the intensity of competition, and others.
Results
During the second stage, the SWOT-analysis weaknesses of the enterprise are studied. It starts with an analysis of the competitiveness of manufactured goods on all markets. As a result, we construct a tree of competitiveness indicators (Filosofova, & Bykov, 2015):
At the 0-th level –a complex index of competitiveness of a particular product;
at the 1st level –a positive effect (integral quality index), total costs, conditions of product use;
at the 2nd level - specific indicators, etc. We calculate in accordance with the constructed tree. Similar performance indicators are collected or forecasted for other competing products. Then weaknesses are defined in connection with company’s strengths defined in the first phase of SWOT analysis.
During the third stage, the SWOT-analysis factors of the firm macro environment (political, economic, technological, market, etc.) are selected. It is done in order to predict the strategic and tactical threats, the firm and timely manner to prevent losses from them.
At the fourth stage, strategic and tactical possibilities of the company (capital, assets, and so on.), necessary to prevent threats, to reduce weaknesses and to increase strengths.
There are 3 primary factors that influence the competitiveness of goods: costs, quality and the cost of the consumer. Marketing activities of the company prioritize what should be done in the first place (Fangmann, 2015):
1) to improve the quality of goods;
2) to reduce costs for the consumer (primarily due to the high quality of the goods and the conditions of its use);
3) to reduce the cost of goods.
To simultaneously improve product quality and reduce costs, it is necessary to apply modern scientific approaches and methods (value analysis, forecasting, simulation, optimization, and others.).
The resource efficiency system sets the following tasks before the company:
•forecasting of demand for products;
•analysis of competition in the market;
•product analysis from the perspective of the consumer;
•parametric, factor and value analysis of products in order to optimize its manufacturing costs;
•marketing research implementation;
•positioning of products in the markets and repositioning;
•analysis of pricing and the price structure;
•analysis of the potential consumption and demand for products;
•formation of the sales system;
•organization of post-service and warranty;
•development of a system of goods promotion to the market and analysis of its effectiveness.
All these functions are designed to be carried out by innovative marketing.
Demand forecasting provides science-based trends of the quality indicators, costs and other indicators used in the development of long-term plans and research and development works. The system of resource efficiency at the enterprise focuses on demand forecasting.
The main demand forecasting tasks include:
•development of forecast of market needs in each specific type of the product in accordance with the results of marketing research;
•identification of the main economic, social, scientific and technological trends, which affect the demand for types of useful effects;
•selection of indicators, which have a significant impact on the value of the useful effects in anticipated new products in the marketplace;
•choice of the forecasting method;
•forecasting new product quality indicators over time taking into account factors that influence them;
•forecasting the organizational and technical level of production at stages of the product life cycle;
•optimization of forecast indicators of quality according to the criterion of the maximum useful effect with a minimum total cost the over product life cycle;
•study of the economic feasibility of developing new products or improving the quality and effectiveness of existing products on the basis of available resources and priorities.
Optimization methods for the analysis of production costs can help solve the problem of resource efficiency at the design stage of product development. Factor analysis sets the degree of influence of factors on the function or feature (useful effect of the machine, the elements of the total cost, productivity, etc.) for the purpose of ranking factors for the development of a plan of organizational and technical measures to improve the function. Value analysis carries out systematic studies of the object (products, processes, structures) in order to increase the useful effects (impact) on the unit of total cost of object over its lifecycle. It also helps to understand whether costs are justified by the resulting properties of the goods that satisfy certain needs and requirements. The peculiarity of the value analysis is to establish the feasibility of a set of functions to be performed by the proposed facility under specific conditions, or the need for the functions of an existing object. One can use a variety of other analytical and methodological tools of marketing to influence resource efficiency.
The concept of social-ethical marketing in management of resource efficiency
The evolution of the concept of marketing has led to the emergence of social and ethical marketing, which has arisen due to environmental degradation, scarcity of natural resources, rapid population growth and the conflict between the needs of the buyer and its long-term well-being. The concept of social-ethical marketing claims that consumers will buy the products of that company which activity is based on determining the needs and wants of target markets and provision of the desired satisfaction by more efficient and more productive ways than those of the competitors, while maintaining and improving consumer and society wellbeing.
Consumers in the process of meeting their needs tend to increase the quality of life, which includes not only the abundance and accessibility of quality goods and services, but also the preservation and improvement of the environmental quality. This led to the need to develop and implement programs of recycling production waste, recycling municipal waste, introduction of new non-waste and energy-saving technologies and other environmentally oriented innovations.
Poor attention of Russian enterprises to environmental protection measures is due to the high cost of their implementation, which could worsen the financial condition of the enterprise. The transition to environmentally oriented marketing is associated with the emergence of a mass movement towards environmental protection.
The concept of social-ethical marketing involves linking within the marketing policy of the three factors: company - consumers - society (fig.
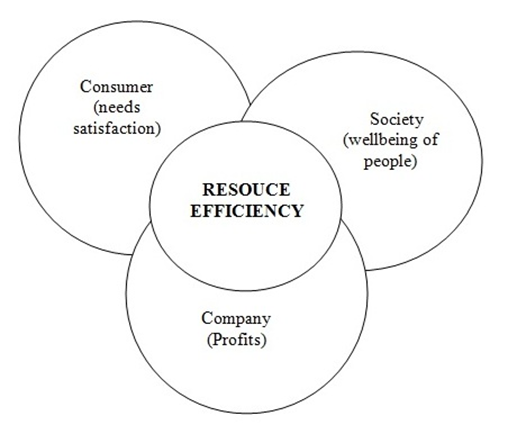
The concept of social-ethical marketing sets certain requirements for resource efficiency management in the organization:
-the main objective of the company - to meet the reasonable needs of customers in accordance with the public interest;
-constant consideration of interests and needs of customers;
-abandonment of production and sale of goods, contrary to the interests of consumers or causing harm to them and society as a whole;
-consumer support of businesses, which provide satisfaction of their normal needs;
-refusal of consumers to buy goods from enterprises, which use environmentally harmful technologies, even when they produce necessary public goods;
-creation and implementation of programs of socio-economic development of the enterprises, which serve not only the interests of the companies and their employees, but also the society as a whole.
Using the concept of social-ethical marketing and competition will inevitably lead to the development of the enterprise resource efficiency management program.
Conclusion
Therefore, marketing as a method for increasing resource efficiency should explore and promote the idea of sustainable use and conservation of resources. Marketing also focuses on the issue of the production of the necessary consumer products demanded by the market, thereby helping to implement the main goals of resource efficiency. Implementation of resource efficiency at the enterprise is based on management of all production processes, as resources are its elements. Thus, marketing is one of the main processes by which we can understand and appreciate the dynamics of the resource efficiency system in the organization.
References
- Andronova, I.V. & Chizhevskaya, Ye.L. (2006). Resursoeffektivnaya strategiya razvitiya: vzaimodeystviye neftyany korporatsiyi regiona. Neftegazovoyedelo. URL: http://www.ogbus.ru (last accessed on 20.04.2012).
- Convis, G. (2001). Role of management in a lean manufacturing environment, Learning to think lean, 01-1014, at URL: http://www.bxlnc.com/download/Role-of-Management-in-a-Lean-Manufacturing-Environment.pdf (last accessed on 29.04.2015).
- Fangmann, G.O. (2015). Marketing innovatsiy: uchebnoye posobiye.-Tomsk: Izd-vo Tomskogo politekhnicheskogo universiteta.
- Filosofova, T. G. & Bykov, V.A. (2015). Konkurentsiya. Innovatsii. Konkurentosposobnost.-Yuniti-Dana.
- Haque, K., Chakrabortty, R.K., Mosharraf, Md., Mondal P. & Anwarul, S. (2012). Implementation of Lean Tools in RMG Sector through Value Stream Mapping (VSM) For Increasing Value-Added Activities, World Journal of Social Sciences, 2(5), 225-234.
- Hill, C.W. L. & Jones, G.R. (1992). Strategic Management. Boston: Houghton Mifflin Co.
- Miller, L.M. (2011). Lean Culture and Leadership Factors A Survey of Lean Implementers’ Perceptions of Execution, URL: http://www.lmmiller.com/wp-content/uploads/2011/06 /Report-Lean-Culture-and-Leadership-Factors4.pdf (last accessed on 29.04.2015).
- Nikulina, I.Ye. (2015). Sovremeny menedzhment. Praktikum: uchebnoye posobiye.- Tomsk: Izd-voTomskogo politekhnicheskogo universiteta.
- Ohno, T. (1988) Toyota Production System – Beyond Large-scale Production, Portland, Oregon, Productivity Press.
- Shah, R. & Ward, P. (2003). Lean manufacturing: Context, practice bundles, and performance. J. Oper. Manag., 21, 129-149.
- Vumek, Dzh. & Dzhons, D. (2005). Berezhlivoye proizvodstvo: kak izbavit'sya ot poter' i dobit'sya protsvetaniya Vashey kompanii.- M.: Al'pinaBiznesBuks.
Copyright information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
About this article
Publication Date
20 July 2017
Article Doi
eBook ISBN
978-1-80296-025-9
Publisher
Future Academy
Volume
26
Print ISBN (optional)
Edition Number
1st Edition
Pages
1-1055
Subjects
Business, public relations, innovation, competition
Cite this article as:
Nikulina, I., Fangmann, G., & Blinov, A. (2017). Marketing As Tool of Resource Efficiency. In K. Anna Yurevna, A. Igor Borisovich, W. Martin de Jong, & M. Nikita Vladimirovich (Eds.), Responsible Research and Innovation, vol 26. European Proceedings of Social and Behavioural Sciences (pp. 706-713). Future Academy. https://doi.org/10.15405/epsbs.2017.07.02.91

