The Relationship of Risk-Recognizing Competency of the Teacher and the Efficiency of Innovative Educational Activities
Abstract
One of the trends in the development of modern education is the focus on its individualization. Focus on student’s personality reveals the contradiction between construction of algorithms that ensure the quality of teacher’s performance, and the increase of the creative component that allows the teacher to go beyond the prescribed work. Under these circumstances, the creative teacher is confronted with numerous risks. Modern trends in the development of teacher education do not disregard the professional readiness of the teacher to innovative activity, but due to different reasons, transformation can not always be successful. This determines the object of our research – the strategy of innovations in teacher training. The study considers the main approaches to innovative scenarios of teacher education. The subject of the research is the teacher’s ability to recognize risks in innovative educational activity (risk-recognizing competency). The aim is to introduce this competency as a tool in enhancing the effectiveness of the teaching performance. The methodology of the research was grounded by the dialectical theory of knowledge and its principles. School teachers admit their incompetency in projecting the innovative process, identifying risks, summing up the results of their activity, minimizing the negative effects of innovations. To sum up, risk-recognizing competency is the "competence of the future". It is aimed at improving the efficiency of innovative educational activities. We consider it as an imperative of educational creativity and of finding non-standard solutions.
Keywords: innovation, innovative educational activity, educational strategy, the strategy of innovative development of teacher education, risk, risk-recognizing competency
Introduction
One of the main factors of progress nowadays above means of goods industry is knowledge and new
ideas that ensure production of competitive intellectual products of high quality. Innovative and
intellectual nature has become one of the main characteristics of the modern economy that provides a
country’s dynamic development and high quality of life.
Pedagogical education is treated as a component of productive forces, meeting, firstly, the needs of
an individual in gaining knowledge, skills, competencies, and secondly, the needs of the economy in
training specialists of pedagogical profile, capable of ensuring reproduction of competitive employees
and formation of human capital.
Problem statement
This trend of social development, according to U. Beck causes a transition from industrial society to
“risk society" (Beck, 1992). In contrast to an industrial society, the characteristic feature of which is the
distribution of benefits, in risk society, there is a tendency of distribution of hazards and forthcoming
risks. Peculiarities of the development of modern pedagogical training discussed above, lead to
strengthening of the role of its individualization.
Research questions
The interest in individualized education in our study is due to the need of definition of risk-
recognizing competency of a future teacher in the content of strategy of innovative development of
pedagogical training. In regard to future teachers’ training for innovative activities we consider
individualization in education as focusing on the development and realization of the potential of each
student in solving life and professional problems and the organization of pedagogical interaction with
regard to individual characteristics of the student and the teacher (Gabdulkhakov, 2013). The choice of
individualization is determined by positioning of the subjectivity paradigm in pedagogics of
professional education.
We regard risk-recognizing competence as the ability of a teacher to set and solve pedagogical tasks
in situations of uncertainty and to minimize negative consequences. In our opinion, pedagogical risk is
a structural component of pedagogical decisions in situations of uncertainty characterized by
consideration of possible alternatives of pedagogical process development, tactics of choice of action
with the aim of optimizing the solution of pedagogical tasks and minimizing negative effects.
In the concept for the long-term socio-economic development of the Russian Federation until 2020,
it is noted that the Russian economy has faced long-term systemic challenges that reflect both the
global trends and internal barriers of development. One of the challenges is the increasing role of
human capital as the main factor of economic development. As a result, the strategic goal of public
policy in education is defined as increasing the availability of quality continuous education in
accordance with the requirements of innovative economic development, the current needs of society
and of every citizen (Concept, 2008). This leads to elaboration of the strategy of innovative
development of pedagogical education.
We consider pedagogical strategy to be the process taking place in time, that is, the set of rational
actions aimed at achieving a certain result in accordance with the intended purpose (Lunev, 2013).
Purpose of the study
The purpose of our study is reasoning of forming undergraduate teacher's risk-recognizing
competency as a tool in enhancing the effectiveness of the innovative teaching performance.
Research methods
For summarizing the theses of the strategy of innovative development of pedagogical education and
the definition of risk-recognizing competency in its structure our study has used the following methods
of scientific and pedagogical research:
- theoretical analysis of research allowing to determine the degree of knowledge on connection of
risk-recognizing competency in teachers with the effectiveness of their innovative pedagogical activity;
- the poll of teachers of secondary schools and students specializing in pedagogical education, aimed
at identifying the relevance and significance of the problem under analysis in teachers’ training
education.
Findings
A procedural nature of pedagogical strategy determines its content (figure 1).
Pedagogical innovations fall into groups on the following grounds:
1) content-target innovations including goal and objectives set, selection and structuring of
educational material, etc.;
2) organizational and technological innovations, combining forms, methods, tools, models,
technologies of training and education, etc.;
3) managerial innovations revealed in the forms and methods of management, network interaction
of educational institutions, regulatory support, etc.
Thus, it is possible to allocate the following components of innovative development strategy of
pedagogical education: content-targeted, organizational and technological, structural and managerial.
In the framework of the development of teachers’ training education these components can be
characterized in the following way.
Content-targeted component, including nomination and scientific justification of pedagogical ideas,
definition of educational content, provides a future teacher with awareness of the need of
transformations in the system of education, a steady focus on the development of pedagogical
innovation and the development of innovative activities.
In our view, innovation is a nonlinear process of transformation of educational systems, combined
with the assertion of such values as initiative, creativity, risk, etc.
Consequently, the attitude of teachers to innovative activity is dubious, since the effectiveness of the
results strongly depends on their professional competence and personal characteristics.

The poll conducted among 459 teachers showed that 78% of them have negative attitude to
innovative activities, explaining that they will have to be in charge of the results of the pedagogical
innovation. Only 22% of respondents admit the need for change in the educational system (table 1).
The results showed that it is possible to speak about psychological barriers in the process of
development of innovative activity. These psychological barriers in the development and dissemination
of pedagogical innovation create risks of falsification and imitation of these innovations as a response
to arising conflicts for teachers. A low level of motivational readiness of teachers is one of these
barriers (Askhadullina, 2015).
The presence of psychological barriers preventing teachers from development and dissemination of
pedagogical innovations is sure to actualize the process of formation of risk-recognizing competency of
an undergraduate teacher as a part of the strategy of pedagogical education innovative development.
The teacher is responsible for training, and in many situations he/she must find ways to reduce this risk
to minimize unexpected and undesirable outcomes (Edelstein, 1998). In our opinion, a teacher should
solve complex professional tasks at a high, holistic and creative level and as well as possible should be
prepared for the designing, implementation, reflection and changing of their educational and
professional reality in accordance with the objective circumstances (Merzon, 2011; Merzon,
Fayzullina, Ibatullin, Krylov, Schepkina, Pavlushkina, & Khairullina, 2015).
Organizational and technological component of the innovative development strategy of pedagogical
education is presented by educational, methodological, psychological and pedagogical maintenance of
competitiveness of institutions engaged in training of specialists of pedagogical profile at regional,
national and international markets of educational services.
It is found that the organizational and technological components lead to the formation of readiness
for innovative activity and professional career of future teachers. Risky character of the teacher’s
pedagogical activity actualizes the need of training teachers capable of effective solving practically
oriented tasks (Panfilova, Panfilov & Merzon, 2015).
Professional career, as a measure of the effective professional role performance is focused on
personal and community success, provides its social media promotion (mobility) and professional
stabilization.
A future teacher implements organizational and technological innovations not only in the framework
of training material, but also as a subject of training. Our experience showed that this ensures a balance
between the assimilation of knowledge, skills development, building competencies associated with the
organizational and technological innovations, and willingness to innovate, the awareness of the need
for reforms in the education system. Future teachers have positive attitudes to innovation.
The research has shown that the professional development of teachers will be successful under the
condition of readiness for innovations. According to N.A. Podymov and L.S. Podymova, it is typical of
beginner teachers to focus on themselves, their feelings, and their behavior. They believe that a young
teacher plucks up a spirit for innovation, in case he/she believes that it would help them feel more
confident (Podymov, 2015).
The poll among 3rd, 4th, 5th -year students specializing in pedagogical education has the following
results (Table 2).
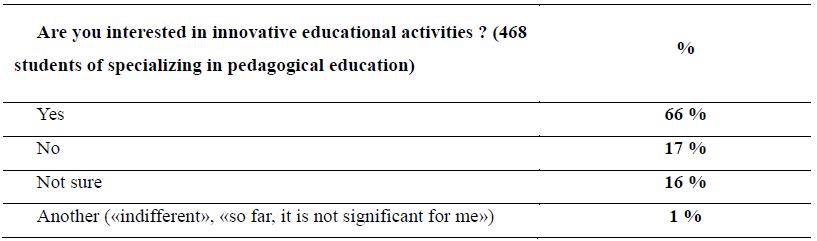
The survey results confirmed the above position of N.A. Podymov and L.S. Podymova about young
teachers’ concentration on themselves, their feelings, and behavior.
Thus, development of risk-recognizing competency in undergraduate teachers, as part of the strategy
of innovative development of pedagogical education, is a relevant issue in the theory and practice of
professional education.
Managerial component of the strategy of innovative development of pedagogical education includes
individualized sets of professional education services, methods of attracting investments into the
system of professional training of specialists of pedagogical profile, the forms of interaction between
educational institutions, the mechanisms of formation and development of the regional market of
professional education services in teacher training, monitoring of quality assurance in professional
preparation of future teachers and their relevance in regional labour markets, modernization of staff
resources in general education.
It is shown that managerial component of the strategy of innovative development of pedagogical
education aims at formation undergraduate teachers’ skills of identification of risks, organization of
innovative activities, summarizing (analyzing), to minimize the extent of negative consequences of
pedagogical innovations.
According to the Professional Standard for Teachers, the set of a teacher's main activities include
readiness for change, mobility, ability for nonstandard actions, responsibility and independence in
decision-making. The authors of this standard have fairly pointed out that one cannot require from a
teacher something he was not ever taught (Professional standard, 2015).
Therefore, the inclusion of training materials on the basis of pedagogical innovation and risking in
undergraduate teachers’ training will contribute to forming skills of designing, identification of risks,
organization of innovative activities, summarizing (analyzing), minimizing the extent of negative
consequences of his actions.
Conclusions
Thus, the development of risk-recognizing competency of a future teacher as part of the strategy of
pedagogical education innovative development is the imperative of development of pedagogical
creativity, search for innovative solutions and responsibility for them.
The content of the strategy of innovative development of pedagogical education is aimed at
positioning it as the basis of the quality of life of an individual, their formation and self-realization, as
well as means of formation of human capital for increasing national competitiveness.
Acknowledgments
The work is performed according to the Russian Government Program of Competitive Growth of Kazan Federal University.
References
Askhadullina, N. N. (2015). Motivational readiness of teachers for innovative activity as a condition of reducing the risks in the process of pedagogical innovations implementation. Kazan Pedagogical Journal, 4(111), part 2, 267-270.
Beck, U. (1992). Risk Society, Towards a New Modernity. Trans. from the German by Mark Ritter, and with an Introduction by Scott Lash and Brian Wynne.
London: Sage Publications. Сoncept of the long-term socio-economic development of the Russian Federation till 2020, approved by decree of the RF Government from 17.11.2008 N 1662-R [Collection of legislation of the Russian Federation, St. 5489].
Edelstein D. (9 Oct. 1998) Low-risk activities. English teaching professional. [Electronic version] http://www.ilkogretimkalbi.com/dokuman/ingilizce/English_Teaching_Professional-/lowrisk.pdf.
Merzon, E.E, Fayzullina, A.R., Ibatullin, R.R., Krylov, D.A., Schepkina, N.K., Pavlushkina, T.V., Khairullina, E.R. (2015). Organizational and Pedagogical Conditions of Academic Mobility Development of Students at School of Higher Professional Education. Review of European Studies, 7(1), 46-51.
Gabdulkhakov, V. F Individualization of professional training in higher education institution: the components of educational technology: monograph. Moscow: Moscow Psycho-Social University (publishing house of NPO "MODEK"); Kazan: Kazan (Volga region) Federal University.
Lunev, A. N., Pugacheva, N. B. (2013). Social practice as the philosophical basis of pedagogical strategizing in a technical University. Society: philosophy, history, culture, 4, 11-16.
Merzon, E. E. (2011). The problem of formation of professional competence of students of pedagogical universities. Journal of scientific publications graduate and doctoral students: research publication. Kursk, 9(63), 81-82.
Panfilova, V.M, Panfilov, A.N. & Merzon, E.E. (2015). Organizational and pedagogical conditions to form the foreign competence in students with the features of linguistic giftedness. International Education Studies, 8(2), 176-185.
Podymov, N. A., Podymova, L. S. (2002). Barriers to innovation (methodological basis of research of relations in the innovation process). Education and science. Journal of theoretical and applied research. [Electronic version]. http://www.jeducation.ru/4_2002/podymows.htm.
Professional standards for teachers (draft) [Electronic version]. http://минобрнауки.рф/документы/3071/файл/1734/12.02.15-Профстандарт_педагога_(проект).pdf.
Copyright information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
About this article
Publication Date
20 July 2016
Article Doi
eBook ISBN
978-1-80296-011-2
Publisher
Future Academy
Volume
12
Print ISBN (optional)
-
Edition Number
1st Edition
Pages
1-451
Subjects
Teacher, teacher training, teaching skills, teaching techniques, organization of education, management of education, FLT, language, language teaching theory, language teaching methods
Cite this article as:
Merzon, E. E., & Askhadullina, N. N. (2016). The Relationship of Risk-Recognizing Competency of the Teacher and the Efficiency of Innovative Educational Activities. In R. Valeeva (Ed.), Teacher Education - IFTE 2016, vol 12. European Proceedings of Social and Behavioural Sciences (pp. 251-258). Future Academy. https://doi.org/10.15405/epsbs.2016.07.40

