Abstract
Ever changing socio-economic conditions impose specific requirements to the system of education, starting from general stage and up to the post-professional education. The article discusses the role and place of a diversified, multi-level system of professional ESL teacher training, which provides a variety of characteristics of educational and self-educational programs that actualizes the problem of improving the system of lifelong general and professional educational environment. ESL teachers being eager to develop themselves and their practice will be a great asset to both, their students and themselves. Successful ESL teachers enhance their professional lives by inservice training programs and postgraduate course, studying for higher ESL teaching qualifications and international certifications. Apart from formal training, however, there is a great deal ESL teachers could do to form their own individual professional educational route within lifelong professional educational environment. The introduced ESL Teacher Development Model provides the effective strategy of combining the forms of formal education, professional socialization and individual self-development within lifelong professional educational environment.
Keywords: Federal Educational Standards, ESL teacher, self-development, lifelong professional educational environment, individual professional educational route, ESL Teacher Development Model, teachers technologies and techniques of teaching and educational work
Introduction
The problem of modern schooling is that teachers due to continual and mechanical repetition of
everyday teaching activities gradually become less and less careful of the modern tasks of foreign
language teaching. More than that, ongoing changes and reforms of the educational system in Russia,
including new Federal Educational Standards introduction, teachers being under the administration
pressure are more engaged in adopting educational programs, writing reports, giving analytical data to
the officials and so on instead of teaching practice and professional self-development are problems.
The other barrier to professional development and self-development is the job qualification demands
reforms. Many teachers nowadays face the problem of official qualification status because of changes
in the job qualifications requirements. For example, according to the university diploma, a teacher
attended courses of Pedagogics and Methods of Teaching and even had the in-service teacher training
practice at school, but it turns out to be not enough now to teach at school because a teacher has not got
the note in the diploma that he or she is a teacher of the definite subject. So professional formal
education could not be a guarantee of getting a job at school.
In addition, teachers could experience financial difficulties being obliged to pay for their additional,
further education or professional retraining. They have to search for some grants and it is also a time-
consuming activity, sometimes they are not free in their choice of professional training course and
educational programs because the government pays their training. Considering that, we can say that
there is no place for the teacher individual professional educational route within current state of
educational environment.
Apart from formal professional education system problems, there is a great deal of restrictions in the
sphere of professional socialization and professional self-development connected with the lack of
necessary information and official support, self-organization and time management skills; poor
physical state and even health problems.
Problem statement
The analysis of ESL teaching experience and educational practice shows that in order to provide
sustainable professional and personal growth, teachers should not concentrate only on knowledge and
skill approach. There are plenty of opportunities of great assistance in making their professional
educational route of development and self-development effective and the lifelong educational
environment beneficial. Though there are a lot of research works devoted to the personality and
professional development and self-development, introducing lifelong educational system, such as
Ushinskii K., Selevko G., Tchoshanov M. and others; the problem of ESL teacher professional
educational development and self-development route within lifelong educational environment still
needs to be thoroughly considered.
Research questions
Is the introduced ESL Teacher Development Model valid or not? Are there significant differences
between current educational environment and the innovative one organized according to the introduced
model?
Purpose of the study
The objective of the research is to present a gist of theoretical analysis of the effective ways of
teachers’ professional self-development within life-long educational environment in accordance with
the new educational standards in the integration of the national education system into the world
educational space. Based on that, the Model of ESL teachers’ professional development and self-
development within life-long educational environment have been introduced and tested (Figure 1).
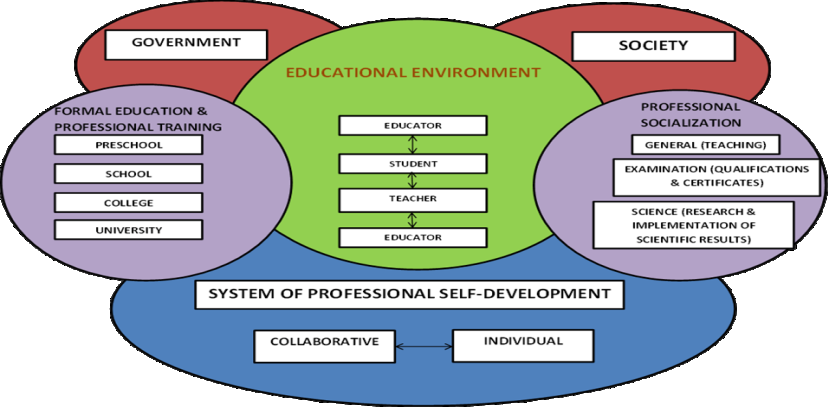
The offered ESL Teacher Development Model should be realized within lifelong educational
environment and is based on Federal State Educational Standards of General Education and
Professional Education including post professional training programs. The important role of
professional socialization should also be taken into consideration when speaking about career
opportunities and professional growth of any educator. Any teacher starting the career has to be aware
of future perspectives, such as international certification, scientific research activity and so on. Lifelong
educational environment supposes the ongoing circle of development and self-development when the
student is in the center of learning process, which starts from the educator as an example and rounds up
with the student becoming a professional educator. So that, teacher is the first step on the way of
becoming an educator, which means not only the possibility to teach at all levels of educational process
(from pre-school to university), but readiness to develop within the world standards of education and
scientific work. At the same time, the process of self-development has got two main forms to support
the educator during all the professional activity: collaborative and individual. Both ways could be
integrated into the process of general and professional education, especially in a form of modules into
the post professional training.
Research methods
The key research methods are the analysis of national educational standards, professional
educational programs and scientific resources, modeling and pedagogical experiment. Base of the
research was provided by means of approbation of ESL Teacher Development Model of teaching and
learning, professional training and self-development within lifelong educational environment during
the implementation of the experimental model in accordance with the new educational standards of
general, professional and post-professional education. In the experiment, there have been schools of
Kazan and Republic of Tatarstan (Russian Federation) under the scientific and educational
management of Kazan Federal University; Institute of Philology and Intercultural Communication of
Kazan Federal University; Volga Region Center for Further Training and Professional Retraining of
Kazan Federal University. Experimental (200) and controlled group (200) of the respondents were
formed from the senior school children (School 122, 75, 9, 165), university students, postgraduates,
school teachers and university lecturers who passed different courses (formal education and additional
collaborative and individual tasks), took part in workshops and project work via distance learning and
within problem-solving projects, methodology seminars and scientific conferences. The research was
conducted within one academic year (from September to June 2015-2016).
Findings
ESL teacher development and self-development could be successful when breaking the well-known
teaching rules or norms as a way of challenging what has been taken for granted. More than that, it
should involve trying out new ideas or changing the ways of using the old ones; investigating
something unknown or even bewildering and frustrating. Overall, in these cases the idea is not only to
improve teacher’s individual performance, but also to learn more about teaching and about the
educational environment itself.
From the Table 1 you can see that schoolchildren and teachers (75% both) are in greater need of
improvement than educators (60%) and lecturers (45%). That means low level of reflection and self-
assessment; the reason might be in the lack of monitoring and management from the side of school and
university administration staff. Nevertheless, such criterion as “understand the necessity” varies greatly
comparing with “in need of improvement” in all groups. For example, senior schoolchildren who
should be ready to choose their educational route show very low level of understanding their needs and
weak points. In this case they could not be ready to both formal educational development and self-
development as the highest level of personality progress. The most problematic is the last criterion
“ready to improve” which shows stable decrease in all groups.
Analyzing the given data we could denote that low level of readiness to develop and self-develop is
the result of the discrete system of general, professional and post professional education. Only a well-
balanced lifelong educational system could provide sustainable growth of development and self-
development intention and readiness.
When speaking about the level of language competence of ESL teacher, we should mention the
tendency to prove that level with the help of international exams. As one of the most popular
international exams in Russia is IELTS, it was used as the instrument for assessment and interpretation
of the research results. Table 2 shows the dependence of the level of English language competence
(given in numbers 1-9 according to the IELTS levels of language competence within Common
European Framework of Reference, level “0” is excluded as most of the experimental and controlled
group respondents have at least level B1) on the level of individual self-development. The dependent
level is typical for all groups; it means that the entire respondent could not continue their development
on the level of self-mode. The educators and lecturers are potentially ready to improve, whereas
teachers and senior school children usually stop when reaching the level which suits them at the
moment. At any rate in all groups, the level of self-development is dependent, so there would not be
any significant progress in English language competence in all groups of respondents. In case of
teachers and senior school children it even could be followed by general digress of the professional
competence in future. When implementing the experimental model of ESL Teacher Development, the
results in the experimental groups have changed greatly within one academic year (the results are
shown in green and orange). As we can see from the table the experimental groups show the stable
tendency to develop their language competence within the formal educational institutes and the level of
self-development has changed to active due to the introducing of the new strategies and educational
technologies into the process of teaching and assessment of the subject, meta-subject and personality
results.
The main educational objective of ESL Teacher Development Model realization is the professional
competence development through different types of professional activities. Creation of conditions for
motivation to further training and development remains to be of paramount importance. For this
purpose, the curriculum of school, university and postgraduate programs of further training and
retraining should include additional disciplines or modules. So, there have been introduced such school
courses for gifted children at schools (senior school children) like “Olympiad training”, “International
Exams training”; constant workshops for school teachers “Main issues of school scientific research”,
“Modern educational technologies in teaching English”; new courses for university students
“Interactive technologies and methods in teaching English”, “CAE course”, “TKT course”; scientific
conferences for educators and lecturers dedicated to the problems of modern testing system, methods
of assessment of language competence. Some of the results of these activities are:
1) Winners of English Language Olympiads at the regional and federal levels;
2) High results in IELTS and TOEFL tests (schoolchildren and university students);
3) Winners at the scientific conferences at the regional and federal levels;
4) Creation of web resources for students and teachers for further self-development
One of the examples of the project work of the students (experimental group) within the university
courses “Interactive technologies and methods in teaching English”, “CAE course”, “TKT course” is
the English Language Teaching – Kazan Federal University blog (http://elt-kfu.blogspot.ru). It could
be a great resource for any educator to gain both motivation to development and experience of
professional activity.
Conclusion
Formation of system of professional development and self-education of ESL teacher within lifelong
educational environment is based on promotion of pedagogical experience at all levels. ESL teacher
experience takes place in the different forms reflected in the experimental model. Thus, the actions are
directed on comprehensive increase of competence and professional skills of ESL teacher, carried out
for mastering teachers technologies and techniques of teaching and educational work, their creative
application on occupations and in extracurricular activities, search of innovative, new and most rational
and effective forms, and methods of the organization, carrying out and analysis of educational process.
Considering internal and external factors of the lifelong educational environment, the existing result
of experimental training allows to speak about the created competence of ESL teacher carrying out
types of professional activity on the level of active self-developing competence.
Acknowledgements
The research was conducted within schools of Republic of Tatarstan and Kazan Federal University. We would like to thank all the students and teachers who collaborated in this research.
References
Atay, D. (2008). Teacher research for professional development.ELT Journal, 62(2)
Biktagirova, G.F., Valeeva, R.A. (2014). Development of the teachers' pedagogical reflection. Life Science Journal, 11 (9), 60-63.
Burton, J., Quirke, P., Reichmann, C. L., & Peyton, J. K. (Eds.). (2009). Reflective writing: A way to lifelong teacher learning. Retrieved from: http://tesl-ej.org/books/reflective_writing.pdf
European Commission: Teacher and Learning (2013). Retrieved from: http://ec.europa.eu/education/policy/school/doc/teachercomp_en.pdf
Schratz, M., Meuret, M., MacBeath, J., Jakobsen L. (2000). Self-Evaluation in European Schools, A Story of Change. London: Routledge Falmer.
Selevko, G. (2006). Encyclopedia of pedagogical technologies. Moscow: NarodnoyeObrazovaniye.
Tatto, M. T., Lerman, S., Novotná J. (2015). Overview of Teacher Education Systems Across the World. The Professional Education and Development of Teachers of Mathematics, Volume 11 of the series New ICMI Study Series, 15-23.
Ushinskii, K. (2005). Pedagogical anthropology. Moscow: Drofa.
Copyright information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
About this article
Publication Date
20 July 2016
Article Doi
eBook ISBN
978-1-80296-011-2
Publisher
Future Academy
Volume
12
Print ISBN (optional)
-
Edition Number
1st Edition
Pages
1-451
Subjects
Teacher, teacher training, teaching skills, teaching techniques, organization of education, management of education, FLT, language, language teaching theory, language teaching methods
Cite this article as:
Khasanova, O. V., & Karimova, A. A. (2016). Esl Teacher Professional Self-development Within Lifelong Educational Environment. In R. Valeeva (Ed.), Teacher Education - IFTE 2016, vol 12. European Proceedings of Social and Behavioural Sciences (pp. 60-66). Future Academy. https://doi.org/10.15405/epsbs.2016.07.11

