Abstract
The research objective is to develop scientific and practical recommendations for enhancing the structure of the service system suitable for use in service sector activities, based on a socioeconomic efficiency evaluation. The implementation of this goal involves the systemic study of the foundations of efficiency in the service sector; the analysis of trends in changes in the parameters of the activities of service organizations based on the evaluation of its socio-economic efficiency; the substantiation of the imperative and strategic directions for the development of service sector organizations and their implementation on an innovative basis. The research methods were the fundamental developments of leading economists on the problems of the functioning of organizations in the service sector and the understanding of the foundations for increasing socio-economic efficiency. The methods of logical analysis and generalization, a systematic, comparative approach, tabular and graphical methods for interpreting trends in the main parameters were used. The application of these methods made it possible to: generalize the essence of the problem of the service sector development, identify the principles of the system of organization of public services; determine methods for assessing their socio-economic efficiency, and scientifically comprehend the problem of their further development based on innovative technological models. The main conclusions were focused on the issues of improving socio-economic efficiency in the service sector, as well as in the analysis of trends in the functioning of organizations providing various types of services, and validation of technological models for increasing in the socio-economic efficiency of service organizations.
Keywords: Evaluation of socio-economic efficiency, innovative methods principles of organization and quality of services, organizations of the service sector, strategies for the service sector development, technological models GAP-model (model: GAP5)
Introduction
The development of the service sector is a necessary prerequisite for the modernization of the national economy to be completed successfully. In developed countries, the enterprises of the service sector have now moved to a new stage of scientific and technological development, which has enabled them to quickly and cost-effectively increase in size and change the structure of the organization, maintain service quality standards and adapt services to the population's needs, and flexibly change the set of social services.
To further increase the efficiency of their development, accumulated experience in the construction and functioning of individual aspects of the public services sector employing new management and social technologies demands scientific understanding. The socio-economic effectiveness of both individual types of services and individual sub-sectors of the service sector must be assessed to achieve successful service sector development. The experience of organising monitoring, auditing, and certification of the services provided, as well as the creation of multifunctional service complexes, whose activities are based on innovative management methods and technologies that can increase enterprises' susceptibility to scientific and technological advances throughout the reproduction cycle, are noteworthy.
The importance of the problem of assessing the effectiveness of the activities of enterprises providing types of services to citizens based on innovative methods and its insufficient work-out at present predetermined the choice of the topic and the relevance of our research. The scientific works of the classics of economics are devoted to the problem of forming a theory of the efficiency of the functioning of the service sector and its socio-economic development. Modern Russian scientists who are actively engaged in this topic include (Dudakova & Gladkova, 2010; Edelev et al., 2009; Petrov et al., 2012; Voloskov, 2020; Vasenkova, 2018; Volkova, 2014) and others.
The theory and practice of performance evaluation in the service sector were studied by (Abramov, 2011; Luneva, 2014; Mabiala & Pantchenko, 2021; Petrov et al., 2012; Protsenko, 2006; Yusupov, 2013) and others. The characteristics of regional service sector development are reflected in the research works of (Gadzhieva, 2017; Gazhur & Lukiyanchuk, 2018; Molev, 2007; Parasuraman et al., 1988; Voloskov, 2020) and others.
Problem Statement
The purpose of this work is to study the directions of improving the efficiency of the trading enterprise's activities, which will give the desired result for the enterprise itself and consumers of its products, reserves and ways are determined to improve the efficiency of a trading enterprise. Effective, that is, effective, gives the necessary and best results in various forms of manifestation (material, monetary, social, etc.). Efficiency is a rather multifaceted concept, which is defined not only from economic but also from philosophical positions (Abramov, 2011; Mabiala & Pantchenko, 2021).
Research Questions
In the context of the objectives of this article, despite the large number of scientific papers devoted to the study of the effectiveness of the functioning of the service sector, some important issues do not have a sufficient level of scientific justification (Gadzhieva, 2017). In particular, factors and forms of manifestation of the effectiveness of public services, existing methods for assessing the effectiveness of the functioning of educational services, and forecasting important indicators of the effectiveness of the functioning of services require a more detailed analysis.
The efficiency of a trading enterprise largely depends on the volume of goods sold. In a transition economy, enterprises are increasing their trade turnover, but it is quite difficult to maintain a positive trend over a long time. The volume of sales is formed under the influence of various factors in the external and internal environment (Shchepakin & Mikhailova, 2020; Vasenkova, 2018). But there are such factors that affect the inefficiency of the organization of a commercial enterprise (inefficient use of retail and warehouse space; low level of service culture; low level of automation; unkempt premises; in most cases, the use of outdated methods of Personnel Management; inefficiency of measures to reduce costs) (Statistical data showcase, 2021; Yusupov, 2013).
The findings are organized in three directions: generic theoretical and methodological underpinnings of the effectiveness and quality of public services, as well as clarification of the features of the formulation of approaches to the study of socio-economic efficiency in the service sector; systematized results of the assessment of the quality of public services; the identified state and prospects for the development of the public service sector; substantiated ways to improve the socio-economic efficiency and quality of public services in health and recreation organizations; in the context of the implementation of the plan and new technical models of public service quality, and developed approaches to increase the efficacy of service organizations.
Purpose of the Study
The objective of this article is to develop theoretical and practical recommendations for improving the service sector, modified for use in service sector organizations, based on an assessment of its socio-economic efficiency and public service quality.
Achieving this goal necessitates completing the following primary tasks:
Research Methods
is enterprises of the service sector and methods to improve their socio-economic relations in the context of innovative transformations. is the improvement of the socio-economic efficiency of the service sector and methods for its evaluation and technological models of its development.
of local and foreign scientists-economists on the problems of the formation and functioning of the service sector provides the theoretical and methodological basis of the research. The abstract-logical technique; analysis, synthesis, observation; and system analysis methodologies were applied during the implementation of the piece. During the implementation of the article, the traditional and specific research methods were used: the abstract-logical method; analysis, synthesis, observation; and methods of system analysis. Other research methods were used, mainly the monographic, the methods of a systematic approach, comparative, economic, logical analysis, and statistical methods, and the index analysis method.
formulated in this work lies in an integrated approach to assessing the socio-economic efficiency and quality of service in the service sector, adapted for use in organizations providing different types of services to the population, based on the use of innovative methods and technologies of modern digitalization of the economy.
The main of them include (Gadzhieva, 2017):
Some of the practical implications of this article's conclusions can be used to build a service sector growth strategy, as well as to improve the forms and techniques of increasing service organizations' socio-economic efficiency.
Findings
The socio-economic efficiency should be considered as the ratio of the results (effects) resulting from the implementation of programs (projects) and the resource costs of their implementation. Regarding the service sector, the results of the implementation of programs can be assessed by three main criteria: economic (financial) efficiency, social efficiency, and socio-economic efficiency. From this point of view, a team of authors led by Andreeva et al. (2014) suggests a scheme of the chain of social results and types of effectiveness (Figure 1).
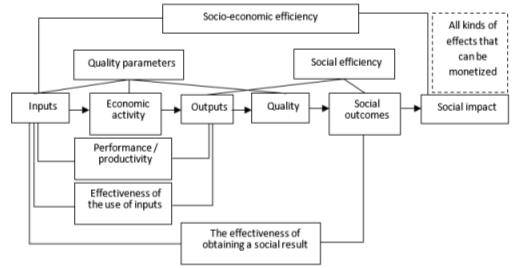
At the same time, economic efficiency is the ratio of the market value of the effects (results) generated by the program and the cost of the resources spent to obtain them. And, from the above, socio-economic effectiveness is a ratio, on the one hand, of social effects (the degree of impact on society), which can be directly measured and expressed in monetary terms, and on the other hand, the costs of implementing socially-significant programs.
The creation of a technique for evaluating the service sector's socio-economic efficiency coincided with the introduction of theories explaining its socio-economic efficiency. The existing methods and technologies for evaluating the effectiveness of the service sector can be divided into two groups: those for determining the contribution to the rate of economic growth or the quality of service in the growth of the gross domestic product, and those for determining the return on investment in the service sector at the micro and macro levels. The indicators used to measure the results of the service sector's operation distinguish the existing approaches (Andreeva et al., 2014).
The emergence of theories explaining the socio-economic efficiency of the service sector was accompanied by the work-out of a methodology for its assessment. The existing methods and technologies for assessing the effectiveness of the service sector can be divided into two groups: those for the contribution to the rate of economic growth or the quality of service in the increase in the gross domestic product (GDP) and those for the return on investment in the service sector at the micro and macro levels. The existing methods can also be distinguished by the indicators used for the results of the functioning of the service sector (Mabiala & Pantchenko, 2021).
In many countries, the share of the service sector is growing rapidly and occupies a very large share in the GDP structure (70-75%); the share of employed (74-79% of the employed population); the share of income from the service sector is about 3/4 of GDP, which is typical for many countries, such as Hong Kong (90%), Luxembourg (85%) and in the USA (76%) and Russia (in recent years – about 60%); in the countries of Southeast Asia – more than 50% of GDP is accounted for by the service sector (Gadzhieva, 2017).
A wide range of service activities, including financial, credit, educational, household, tourism, medical, telecommunications, and other services, give a high level of growth in the service sector for economically developed countries. The service sector in developing economies is frequently dominated by particular types of service-related activities, such as tourism, the banking and credit system, transportation, and a few other service sectors (The service sector in Russia, 2020).
Modern trends in the digitalization of the economy have caused the rapid growth of the tertiary sector, creating an infrastructure base to support the activities of enterprises in the primary and secondary spheres of activity. In addition, many authors argue that the active development of the service sector is due to the influence of several factors, among which are government policy, business trends, information technology development, social changes, etc. (Mabiala & Pantchenko, 2021; Parasuraman et al., 1988).
Currently, the word "service sector" is vague. There are numerous alternative definitions of the service sector in Russian literature, ranging from two categorical definitions , one of which is based on the premise of providing services primarily to people, that is, it is a collection of industries, sub-sectors, and activities whose functional purpose in the system of social production is expressed in the production and sale of services to people (Edelev et al., 2009; Vasenkova, 2018).
It is this understanding of the service sector that conveys a more precise meaning for our research. The service sector is a set of economic sectors that provide services to the population. It is directly related to the reproduction of human life and contributes to the creation of favourable conditions for the development and placement of productive forces in individual regions (Gamidova, 2021; Petrov et al., 2012).
The service sector encompasses a significant number of activities grouped according to various classifications used at both the international and national levels. According to the WHO classification, there are more than 150 types of services grouped into twelve sectors. At the same time, in terms of their structure and volume of consumption, the leaders are utilities – 21.2%, transport services – 20%, and communication services – 19.5% of the total consumption of services in 2010 (Volkova, 2014).
The main branches of the Russian service sector are (The service sector in Russia, 2020):
The trade deals with the purchase and sale of goods and the provision of several services to the buyer. The total volume of retail trade operations during 2021 amounted to 33,532.1 billion rubles, which indicates its constant growth over the past decades. The number of retail outlets has increased significantly, network companies have emerged, numerous super- and hypermarkets have opened, and Internet-based commerce has grown.
In the modern sphere of transport, there is a giant network that allows for a trillion ton-kilometers of cargo turnover (5,6691 in 2021) and establishes a flow of billions of passenger-kilometers (531,9 in 2020). Railway and pipeline modes of transport are intensively developing.
This is a rapidly developing and most promising service sector that deals with the problems of information transmission on an innovative basis. The total number of cellular subscribers in Russia, whose services are currently provided by: MTS, MegaFon, and Volna Mobile for the first half of 2021, amounted to 260.647 million people. The total number of Russian Internet users for 2021 reached 109.6 million, and the absolute majority of them (86%) visit this information resource daily.
In addition, according to 2020 data (The service sector in Russia, 2020): 25.8 million Russians have fixed-line telephone service; 34.9 million have broadband internet access, and 27.4 million are subscribers to television services. The total financial revenue of telecommunications companies amounted to 1.636 billion rubles at the end of the year.
The modern financial system of Russia operates in the conditions of station processes, adapting to the conditions of digitalization of the financial and banking economy, and today the total number of employees in the financial sector exceeds 1 million people. The finances of Russia by the end of 2021 are (The service sector in Russia, 2020):
Russia has huge potential for tourism development. The number of foreign citizens who visited Russia in 2021 amounted to 32.9 million, of which 5.1 million arrived for tourist purposes, which led to an increase in the tourist flow by 20.5%.
Russia's tourism industry can always offer its clients visits to over 100 resorts located (The service sector in Russia, 2020):
. Basically, the social sphere in Russia is represented by the education and healthcare systems. 16 million schoolchildren, 1 million teachers, and 7 million students (4,161.7 in the university system, 2,995.8 in the secondary vocational education system) started the learning process in 2021, intending to master 3,326 trillion rubles.
A simple analysis shows the steady growth dynamics of those areas that initially had a good material base, traditionally established connections, a high level of demand, and did not require significant funding. Since 2018, the share of the service sector in the nominal volume of the gross value added (GVA) has fluctuated between 46.6-48.8%, and in 2021 it amounted to 48.8%, which is significantly lower than the share of the service sector in the economies of developed countries. The less-developed service sector in Russia makes it difficult to carry out the socio-economic functions assigned to it. The changes in the service sector are reflected in its structure (Table 1).
Source: compiled by authors based on the data of Russian statistics services (The service sector in Russia 2020; Statistical data showcase, 2021)
It is shown in the table, the share of utilities and communication services in the paid service structure has risen since 2018, while the share of transportation and residential services has declined. Other services accounted for nearly the same percentage of the total. These changes reflect current societal trends: utility rates have risen dramatically, society is becoming more informatized, demand for communication services is expanding, and a growing proportion of the population is purchasing their transportation. The analysis of statistical data on the provision of paid services in Russia clearly illustrates the uneven distribution of service enterprises, which is reflected in the significant difference in the volume of sales by federal districts (Table 2).
Source: compiled by authors based on (Statistical data showcase, 2021).
It can be seen from the table, the main share of the production of paid services falls on the Central Federal District. In other districts, the situation is approximately the same. The uneven distribution of enterprises in the service sector is associated with various factors in the placement of enterprises. In 2021, the largest share of paid services to the population of 35.1% is noted in the Central Federal District and the smallest share of 5.9% is in the Far Eastern Federal District.
Furthermore, it is critical to develop the conditions and the methods for evaluating service quality in the context of service sector development, as well as methodological approaches for the analysis and evaluation of socio-economic efficiency in the service sector, thereby bolstering the prospects for the implementation of a model programme for the development of a recreation and wellness system in the service sector (Gadzhieva, 2017).
When evaluating a service, five stages affect the evaluation of the quality of its provision, which can be defined as the intervals between expected and actual service (Plotnikova & Volkova, 2014; Voloskov, 2020; Yusupov, 2013):
In addition, a systematic analysis of the effectiveness of the service sector needs to determine the criteria (factors) for its evaluation, which include: reliability, accessibility, reputation, the responsiveness of employees, competence, politeness, communication, etc. (Knyazheva, 2014; Luneva, 2014).
Traditional models aren't complete, and various academics are still working on them. As a result, the updated model now contains five new components: ideal standards, translation of strategy and policy into service quality specifications, service quality strategy and policy, employee perceptions of customers, and management perceptions of customers (Andreeva et al., 2014).
Regarding the identification of methodological approaches to the evaluation of socio-economic efficiency in service industries, many authors confirm that "achieving efficiency is one of the main problems to be solved because it affects all spheres of society". Economic efficiency in the service sector is an integral element of the overall efficiency of public labour and is expressed by certain criteria and indicators (Klyushkin & Zhukovskaya, 2018).
The approaches to determining the effectiveness of services have been considered by Knyazheva (2014) and Kononova (2012), they highlight:
Within the framework of this approach, the author identifies the following performance indicators (Mabiala & Pantchenko, 2021):
The problem of determining the efficacy of the service sector has a variety of methodological techniques. When it comes to methods for assessing the service sector's socioeconomic efficiency, we can point to (Andreeva et al., 2014; Luneva, 2014; Mabiala & Pantchenko, 2021; Molev, 2007; Shchepakin & Mikhailova, 2020; Voloskov, 2020; Yusupov, 2013):
"systematizes the provision of such services, at relatively lower costs and with rational use of available resources, to ensure the fullest provision of high-quality services to the population" (Mustafayeva & Tatuev, 2004, pp. 25).
" to evaluating the effectiveness of the service sector is characterized by the ratio between the results achieved and the costs of various resources available to society (the "costs-resources" approach)" (Yusupov, 2013, pp. 5-6).
"The third approach considers the effectiveness of the service as the degree of satisfaction with them. The consumer considers their quality to be the main indicator of the efficiency of the services consumed" (Gamidova, 2021, pp. 70-72).
"The fourth, goal-oriented approach, allows us to compare how well the company has fulfilled the goals set initially. The list of such goals usually boils down to the following" (Andreeva et al., 2014, p. 67; Yusupov, 2013, p. 6):
It is advisable to take a methodical approach to address service sector efficiency issues. The author Abramov (2011), Yusupov (2013), Voloskov (2020), Kononova (2012) provided a systematic method that involves the formulation of different criteria and indicators for different levels of management and a specified hierarchy of goals and, consequently, effectiveness criteria:
A number of critical indicators are reflected in figure 2 in the technique for evaluating the socio-economic efficiency of service provision. According to Figure 1, indices of socio-economic efficiency include an increase in the physical volume of services delivered, a drop in overall expenses and other factors.
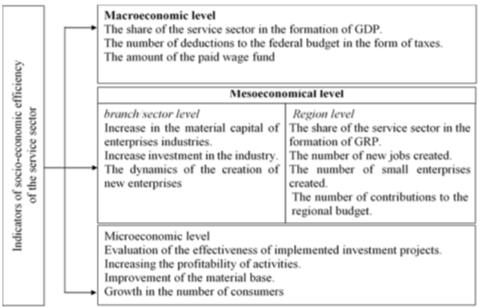
The measures of social efficiency reflect the quantitative side of social goals attained, such as the creation of new services, changes in the consumer price index, improved quality of life, reduced unemployment, increased fertility, and decreased mortality (Abramov, 2011; Voloskov, 2020; Yusupov, 2013). The size of the wage fund for employees of the enterprise, including social contributions; the number of employees of service sector enterprises; the number of tax payments to budgets at various levels made by the enterprise providing services; the profitability of service sector organizations should all be considered when determining the socio-economic efficiency of the service sector.
The following metrics should be considered when assessing the service sector's socioeconomic efficiency:
The size of the wage budget for the enterprise's employees, including social contributions; the number of service sector employees.
The total amount of tax payments made by a service provider to various budgets at various levels.
The following indicators can be used to gauge the service sector's development:
In order to assess the service sector's economic efficiency, we believe it is necessary to add an indicator of the industry's investment activity, which indicates investment intensity and is defined by the ratio of investment to revenue for the same time (Abramov, 2011):
(1)
where – denotes the industry's investment activity; I – denotes the total volume of investments made in the industry over a certain period of time; V – denotes the amount of revenue generated by sales in the industry over the same period of time.
We recommend considering some metrics of the industry's socio-economic efficiency for the convenience and speed of comparison of the following indicators (Yusupov, 2013):
(2)
where – a complex indicator of the socio-economic efficiency of the industry; i = 1 ... n – the studied indicators; – the index of the branch of the national economy; – the coefficient of the significance of the-th indicator, a fraction of a unit; – the analyzed indicator reflecting the social or economic effect in the industry; – the average value of the indicator for all industries.
It should be mentioned that, based on the study's aims, the collection of analyzed performance indicators might be enlarged at the discretion of the experts. Experts' opinions on the significance of each indication are based on their theoretical knowledge and practical experience. Let's look at the indicators for the southern federal district's areas from 2018 to 2021. Table 3 shows the data that will be used in the analysis. The Krasnodar Territory and the Volgograd Region are the leaders in the development of the service sector in the Southern Federal District, according to the data in the table. To get more precise answers, we use the method to generate a sophisticated index of the region's socio-economic efficiency.
It should be mentioned that, based on the study's aims, the collection of analyzed performance indicators might be enlarged at the discretion of the experts. Experts' opinions on the significance of each indication are based on their theoretical knowledge and practical experience. Let's look at the indicators for the southern federal district's areas from 2018 to 2021. Table 3 shows the data that will be used in the analysis. The Krasnodar Territory and the Volgograd Region are the leaders in the development of the service sector in the Southern Federal District, according to the data in the table. To get more precise answers, we use the method to generate a sophisticated index of the region's socio-economic efficiency (2). The region of the southern federal district is the indicator j in this case (Gadzhieva, 2017).

The following values will decide the relevance of the indicators:
The measures that contribute to the development of the regional service sector include the following: stimulation of innovation and investment activities in the industry; ensuring the availability of all types of services in terms of territorial location, modes of operation, and methods of service; application of a differentiated approach to pricing, taking into account privileged categories of the population; creation of a network of municipal agents providing services to vulnerable groups of the population, etc. Based on what has been said and based on the ongoing processes of digital transformation of the socio-economic life of the country, an important point is the identification of technological models for improving the efficiency of the organization of the service sector (Vasenkova, 2018; Volkova, 2014).
The results of calculations using the proposed method show that higher development and efficiency in the service sector are observed in the Volgograd Region and the Krasnodar Territory. The Rostov region immediately follows the leaders and is in third place. This indicates the need to pay more attention to the development of the service sector in the region.
Source: compiled by authors based on S.S. Abramov’s research (2011).
A complete approach for assessing the efficacy of service supply by firms whose activities are controlled at the regional level should be included in the quality management system and used as a metric for assessing management effectiveness. Improving the service sector's socio-economic efficiency will result in increases in the following metrics for a given region: regional gross product; tax revenues to the government; self-employed population earnings; and able-bodied person employment (Gadzhieva, 2017).
From all of the above, it is clear that the coronavirus pandemic posed a serious obstacle to the service sector's active socioeconomic development: many service-related businesses were unable to cope with the crisis caused by COVID-19, because hairdressers', beauty salons', and catering services could not be implemented in an online format, such as educational services. As a result, the demand for them decreased by 70% (Kapuschak & Kharitonova, 2021), which led to an increase in the number of unemployed. Thus, in May 2020, the unemployment rate among representatives of the service sector reached its maximum value of 6.1% (Kapuschak & Kharitonova, 2021).
Conclusion
The development of the service sector generates the need to assess its socio-economic efficiency. As for the problems of its assessment, a certain methodology is proposed, using indicators that allow for a comprehensive analysis of the socio-economic efficiency of the activities of service organizations. And, on the example of some regions of the Southern Federal District, conclusions are drawn and the need for measures to promote the development of the service sector is substantiated:
In modern practice, changes in the service sector are either extensive or intensive. These areas of change are not accompanied by the formation of a new potential of service sector enterprises, focused on future transformations of value orientations and consumer preferences, which are possible only through innovative activities. The latter provides enterprises in this area with a stable position in the market throughout the entire life cycle of goods and services, allowing for flexible manoeuvring in the provision of services to consumers in a situation of uncertainty. We are talking about a constantly updated process of transformation of the service sector.
This process, in our opinion, is multifaceted and includes issues of strategic planning and management, activation of scientific research, marketing, organizational design of the service sector, and the formation of a team of performers whose activities are innovative. It can be said that the innovative process of forming the service sector is adequate for the consumer market when there is an understanding of the causes, significance, and necessary direction of innovations, their scope, degree of novelty, and the specifics of the life cycle structure, the depth and scale of changes, as well as differences in meeting needs. in certain segments of the consumer services market.
As a result, innovation activity can be characterized as the activity of implementing in industries, organizations, and the economy a wide range of innovations related to:
Consequently, innovation activity acts as organizational and managerial support for the implementation of all stages of the product life cycle. The scope of innovation management tasks is expanding and involves providing marketing support for innovation and managing the intellectual property being created, organizing investment in innovation, and overcoming resistance to change on the part of the staff. All this requires the formation of a methodological and practical justification and the development of adequate tools. Underestimation of the features of innovation activity and insufficient development of theory and methodology in the service sector have led to a significant decrease in the efficiency and effectiveness of innovation, which often affects the competitiveness of an organization.
Thus, the organization of the innovative activities of enterprises representing the service sector should ensure, firstly, the achievement of a common vision of the supply of services in the consumer market; secondly, the definition of strategic priorities in the transformation of this area; thirdly, the development of a strategy for the activities of enterprises in the long term; fourthly, the creation of a communication system focused on the implementation of services; fifthly, the formation of innovative personnel with the definition of areas of responsibility for the results of work; and sixth, the introduction of the system controlling the processes of services in the consumer market.
One of the main trends in socio-economic development is the growing importance of the service sector. To build an effective competitive environment in which it is advisable for economic agents to consider their organizational and economic characteristics, rely on their competitive advantages, develop them, and use modern digital technologies. Of course, the organizations of the Russian service sector win and hold their positions in different ways. In order to compete more successfully with the leading tourist countries, the Russian service industry should not only make more extensive use of national advantages but also develop the domestic market for digital, information, and telecommunication services, which will allow many Russian organizations to more effectively carry out their activities online.
In our opinion, the implementation of the selected areas will create conditions for the expansion of the service market and strengthen the competitive position and advantages of service enterprises.
References
Abramov, S. S. (2011). Ocenka social'no-ekonomicheskoj effektivnosti sfery uslug v regione. Regional'nye i otraslevye ekonomicheskie [Assessment of socio-economic efficiency of the service sector in the region]. Regional and Sectoral Economic. Scientific and technical statements of SPbGPU. Economic Sciences, 3, 41-42. https://cyberleninka.ru/article/n/otsenka-sotsialno-ekonomicheskoy-effektivnosti-sfery-uslug-regiona/viewer
Andreeva, E. I., Gorshkova, D. I., & Kovalevskaya, A. S. (2014). Rekomendacii po ocenke social'no ekonomicheskoj effektivnosti social'nyh programm. Opredeleniya, podhody, prakticheskij opyt [Recommendations for assessing the socio-economic efficiency of social programs. Definitions, approaches, practical experience]. Prospect Publishing House. https://ep.org.ru/wp-content/uploads/2015/02/ozenka_soc-economy_effectivnosty.pdf
Dudakova, I. A., & Gladkova, Yu. V. (2010). Innovacionnoe razvitie sfery uslug rossii kak osnova postroeniya servisnoj ekonomiki [Innovative development of the Russian service sector as a basis for building a service economy]. Bulletin of DSTU, 6(49). https://www.vestnik-donstu.ru/jour/article/viewFile/1060/1055
Edelev, D. A. Tatuev, A. A., Novoselov S. N., Breslavtseva, N. A., Klyukovich Z. A., Radina, O. I., Rossinskaya, M. V., Beryoza, N. V., Abramov, S. S., Buryakov, G. A., Golik, E. N., Breusova, E. A., Skrynnikova, I. A., Shevchenko, E. V., & Savchishkina, E. P. (2009). Nauchnye i organizacionno-ekonomicheskie aspekty genezisa, formirovaniya i razvitiya sfery uslug [Scientific and organizational-economic aspects of the genesis, formation, and development of the service sector. South Russian State University of Economics and Service. elibrary.ru/item.asp?id=19918606
Gadzhieva, A. (2017). Sovremennaya sfera uslug: klassifikaciya i rol' v ekonomike [Modern service sector: classification and role in the economy]. Russian Economic journal, 6, 67-78. https://www.elibrary.ru/item.asp?id=32587157
Gamidova, N. Z. (2021). O zashchite prav potrebitelej v sfere okazaniya uslug [On the protection of consumer rights in the provision of services]. Public service and personnel, 3, 70-72. https://www.elibrary.ru/item.asp?id=46582136
Gazhur, A. A., & Lukiyanchuk, I. N. (2018). Tendencii razvitiya sfery uslug v Rossii [Trends in the development of the service sector in Russia]. Bulletin of the Voronezh State University of Engineering Technologies, 80(3), 444-450. DOI:
Kapuschak, I. Ya., & Kharitonova, N. A. (2021). Rossijskij sektor uslug: sovremennoe sostoyanie i osnovnye tendencii razvitiya [Russian service sector: current state and main development trends]. Service in Russia and abroad, 15(1), 24-35. DOI:
Klyushkin, A. I., & Zhukovskaya, I. V. (2018). Metodologiya «Cost Gap» kak innovacionnyj metod upravleniya sferoj uslug v usloviyah krizisa [Methodology of "Cost Gap" as an innovative method of management of service sector in a crisis]. Microeconomics, 1, 35-40. https://www.elibrary.ru/item.asp?id=32574779
Knyazheva, Y. V. (2014). Povyshenie effektivnosti sistemy massovogo obsluzhivaniya torgovogo predpriyatiya posredstvom chislennogo statisticheskogo modelirovaniya [Improving the efficiency of the queuing system of a commercial enterprise through numerical statistical modelling]. Bulletin of novosibirsk state university. series: socio-economic sciences. 14(2), 83-100. https://www.elibrary.ru/item.asp?id=21969385
Kononova, I. V. (2012). Social'no - ekonomicheskaya effektivnost' i kachestvo obsluzhivaniya naseleniya v sfere rekreacii turizma [Socio-economic efficiency and quality of public services in the field of recreation tourism]. Vector of science of togliatti state university, 1(19), 147-151. https://elibrary.ru/item.asp?id=17733560
Luneva, E. I. (2014). Kriterii kachestva i effektivnost' predpriyatij industrii uslug [Quality criteria and efficiency of service industry enterprises]. Standards and quality, 11, 48-51. https://www.elibrary.ru/item.asp?id=22489373
Mabiala, G., & Pantchenko, E. E. (2021). Analiz napravlenij povysheniya effektivnosti ispol'zovaniya resursnogo potenciala predpriyatiya [Analysis of directions for improving the efficiency of using the resource potential of the enterprise]. Collection of articles of the International Scientific and Practical Conference: Modern technologies in the world scientific space, 110-112. https://os-russia.com/SBORNIKI/KON-367.pdf
Molev, M. D. (2007). Regional'naya sfera obsluzhivaniya: koncepciya razvitiya [Regional service sector: development concept]. South Russian State University of Economics and Service, Shakhty, service plus, 3, 29-32. https://www.elibrary.ru/item.asp?id=12915209
Mustafayeva, Z. A., & Tatuev, A. A. (2004). Issues of functioning and development of the service sector. MES RF, Feder. Agency for Education, Kabard.-Balk. gos. un-T. K.-Balk GU.
Parasuraman, A., Zeithaml, V. A., & Berry L. L. (1988). SERVQUAL: A multiple- Item Scale for measuring consumer perceptions of service quality. Journal of Retailing, 64(1), 12-40. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/225083802_SERVQUAL_A_multiple-_Item_Scale_for_measuring_consumer_perceptions_of_service_quality
Petrov, A. N., Karpova, G. A., & Khoreva, L. V. (2012). Konceptualizaciya podhodov k formirovaniyu celostnoj teorii uslug [Conceptualization of approaches to the formation of a holistic theory of services]. Proceedings of the st. Petersburg university of economics and finance, 1(73), 40-50. https://www.elibrary.ru/item.asp?id=17571489
Plotnikova, V., & Volkova, A. (2014). Service Economy and the Specifics of its Development in Russia. Procedia Economics and Finance, 6, 18-23. DOI: 10.1016/S2212-5671(14)00769-2
Protsenko, S. (2006). Evaluation of satisfaction with the quality of services. "Sales business, 4. Retrieved on February 25, 2022 from https://arhivinfo.ru/1-34014.html
Shchepakin, M. B., & Mikhailova, V. M. (2020). Sektor uslug kak ekonomicheskaya kategoriya i vid ekonomicheskoj deyatel'nosti [The service sector as an economic category and type of economic activity]. Economics, entrepreneurship and law, 10(1), 71-88. https://1economic.ru/gr/epp-papers/41545.pdf
Statistical data showcase. (2021). Retrieved on 25 May, 2022 from https://showdata.gks.ru/finder/descriptors/275422
The service sector in Russia. (2020). Retrieved on 25 May, 2022 from https://xn--80aegj1b5e.xn--p1ai/publication/sfera-uslug-v-rossii#osnovnye-tendencii-razvitiya-sfery-uslug-v-rossii
Vasenkova, E. I. (2018). Service sector development and economic growth. 9th International Workshop AMADE, 1-2. https://elib.bsu.by/bitstream/123456789/207305/1/Васенкова.pdf
Volkova, A. A. (2014). Sfera uslug: teoreticheskij analiz [Sector of services: Theoretical analysis]. Proceedings of the st. Petersburg state university of economics, 4(88), 11-16. https://www.elibrary.ru/item.asp?id=21975699
Voloskov, A. B. (2020). Mesto i rol' sektora uslug v dostizhenii Strategicheskih nacional'nyh celej [The Place and Role of the Service Sector in Achieving Strategic National Goals]. Macroeconomic analysis: methods and results. World of Economics and Management, 20(4), 78-98. DOI:
Yusupov, R. M. (2013). Metodicheskie aspekty ocenki effektivnosti deyatel'nosti predpriyatij i organizacij sfery uslug v sovremennyh usloviyah innovacionnogo razvitiya ekonomiki [Methodological aspects of assessing the efficiency of the activities of enterprises and organizations in the service industry in modern conditions of innovative development of the economy]. Management of economic systems: electronic scientific journal, 12(60), 1-10. https://www.elibrary.ru/item.asp?id=21438884
Copyright information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
About this article
Publication Date
29 August 2022
Article Doi
eBook ISBN
978-1-80296-126-3
Publisher
European Publisher
Volume
127
Print ISBN (optional)
-
Edition Number
1st Edition
Pages
1-496
Subjects
Economics, social trends, sustainability, modern society, behavioural sciences, education
Cite this article as:
Mabiala, G., Lynskiy, D. V., Bayrakova, I. V., Romaniuk, E. V., & Kochetkova, N. V. (2022). Sociо-Economic And Technological Models For Increasing Efficiency Of Service Sector Organizations. In I. Kovalev, & A. Voroshilova (Eds.), Economic and Social Trends for Sustainability of Modern Society (ICEST-III 2022), vol 127. European Proceedings of Social and Behavioural Sciences (pp. 479-496). European Publisher. https://doi.org/10.15405/epsbs.2022.08.52

