Abstract
One of the important factors in increasing the efficiency of small and medium-sized businesses and maintaining their competitiveness is the implementation of innovative activities. Most entrepreneurs are always interested in innovative activities. However, having chosen an innovative business, it is necessary to study all of its features, since the difficulties arising in the implementation of entrepreneurial activity are reflected in the innovation sphere. One of the problems of innovative activity among small and medium-sized enterprises, as a rule, is the lack of material and technical base. Often, their funds are insufficient and, in order to successfully implement innovative projects, there is a need for outside support. Stimulation of innovative activities of business entities by the state is carried out through forms of incentives. Based on the analysis of existing state programs containing various forms of stimulating innovative activity, as well as regulatory legal acts establishing the procedure for their provision, provisions were identified that were taken as criteria for choosing the optimal forms of state support. The use of the considered criteria will make it possible to choose suitable forms of stimulating innovation activity by small and medium-sized enterprises, ensuring the effective implementation of innovative projects, taking into account the complexity of the implementation of the innovation process and the characteristics of the enterprise.
Keywords: innovative activity, small and medium business
Introduction
The introduction and development of innovations over a long period of time is one of the fundamental factors in increasing the efficiency of small and medium-sized businesses and a priority area of state economic policy (Federal Law No, 2014; Federal Law No,1996; Federal Law No, 2007). Often, the possibility of implementing innovative projects is in no way connected with business, since the innovation process involves research and development activities, significant financial investments. In most cases, entrepreneurship is associated only with the provision of services and a small scale of activity. Of course, most small and medium-sized businesses are not associated with the implementation of investment projects that can be implemented by large enterprises, however, certain types of innovations, related, for example, to modification, improvement, development in certain industries, are available to the business sector.
Problem Statement
Possessing undeniable advantages in the implementation of innovative processes due to the mobility of the transition to innovative projects, with a precise focus and narrow specialization, as well as other factors, the sphere of small and medium-sized businesses is becoming more and more attractive for the implementation of innovations (Resolution, 2017; Tishchenko,2018). However, the implementation of innovative projects by business entities is associated with certain difficulties and risks.
Today, most of the problems associated with business development are caused by the shortcomings of state economic policy, since the parameters of the external environment where small business development takes place largely depends on it. The indisputable fact is that business entities in the implementation of innovative activities need constant support from government bodies. Currently, there are various programs of state support that contain a significant number of forms and methods (economic, financial, tax) to stimulate innovation (Galcheva, 2020; Government of the Russian Federation, 1999; Passport of the national project, 2018; Saakyan, 2014a; Saakyan, 2014b; Vlasova et al., 2019).
There is a need to study the existing forms of support, their choice and the possibility of their use
Research Questions
The analysis of the existing forms of incentives made it possible to identify the main criteria underlying each of them, namely: the conditions of provision; basis of provision; order of receipt; term of receipt of the incentive form; the period for which the incentive form is provided (Department of State Target Programs and Capital Investments of the Ministry of Economic Development of the Russian Federation, 2020). In addition, speaking about the innovative activities of small and medium-sized businesses, an important addition is such criteria as: location of the enterprise; risks arising at the stages of the innovation process.
Purpose of the Study
As already noted, state support for innovative activities of business entities contains a set of measures developed by both federal and regional legislation. However, enterprises often do not have complete information about the existing forms of state support, about the possibilities of their use, about additional benefits. Many business entities need assistance, which consists in consulting, clarification of regulatory legal acts that establish the rules and procedures for the application of forms of state support, in the provision of premises and/or equipment for the implementation of innovative activities, in additional financial resources.
The probability of success of an innovation is directly related to the speed of implementation of the innovation process . Sometimes the implementation of an innovation is extended over a long period. And during this time, other types of competitive innovations can be developed, as a result of which the product will no longer have great value. Therefore, in order to successfully implement innovative activities, it is important to understand at what stage an enterprise needs government support and, if the need arises, then by what form of stimulation.
Research Methods
Having considered the current state of innovative activities of small and medium-sized businesses and having analyzed the existing forms of incentives and formulating the criteria for their selection in order to identify the most optimal and preferable, an algorithm has been developed.
Findings
Let us consider the procedure for choosing the forms of stimulating innovation through the algorithm presented in Figure 1.
The location of the business entity is one of the important criteria. There are technical and innovative special economic zones (TISEZ), which are intended for the development of subjects of the innovation sphere, the development and implementation of scientific products (Federal Law No, 2005). If an economic entity has the right to become a resident of such a zone, it is provided with additional benefits, special conditions prescribed in the relevant legislative acts, which facilitate the conduct of innovative activities (Portal of the Innovation Promotion Fund, 2020).
If a small and medium-sized enterprise (SME) is not a resident of a TISEZ, then in order to choose a form of incentive, the following criterion is considered—the stage of innovative activity (IA).
When considering this criterion, the activities of the enterprise play an important role. For example, an enterprise is engaged only in fundamental research (FR) and research and development (R&D), or vice versa, only in experimental design (ED).
Financial support of projects can be carried out at any stage of innovation activity on a non-refundable basis (NR), i.e. provision of funds for a certain time without a refund, or on a repayable basis (RP), i.e. provision of various funds for a specific time with the obligation to return them by a specified date with interest payment.
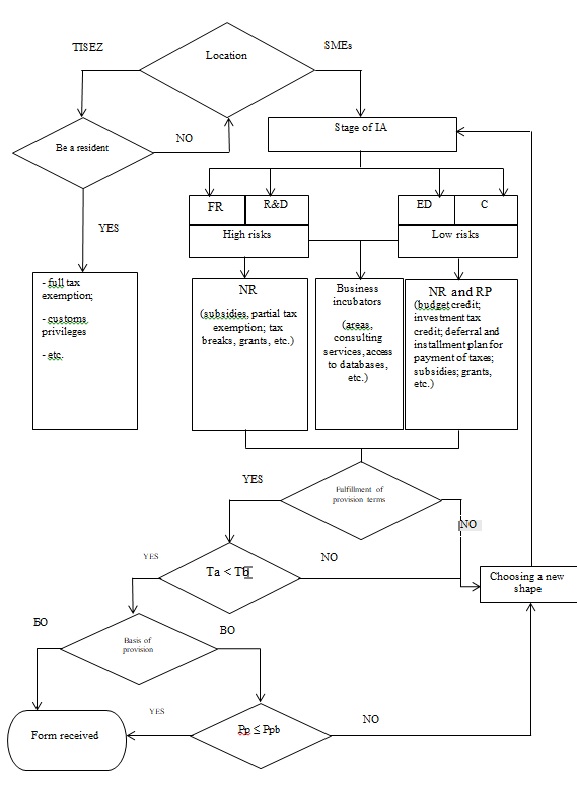
Each stage of the innovation process has its own risks. At the stage of fundamental research and research, as a rule, the risks are very high due to the high degree of probability of negative results. At such stages, preference is given to forms on a non-refundable basis of provision, it is more favorable for stimulating the innovation activity of enterprises (for example, such forms as budget allocations, government subsidies, extra-budgetary funds, grants and other forms).
At the stages of development and commercialization (C) risks are reduced, and it is possible to consider forms of incentives provided both on a non-refundable basis and on a refundable basis. In addition, at any stage there is an opportunity to get support from regional business incubators by becoming their resident. The main activity of business incubators is provision to residents of equipped office space; provision of services for organizational support of residents; assistance in organizing business and in attracting financial resources to the project.
If any of the provisions is not met, the entrepreneur considers another form of incentive. If all the conditions are met, the following criterion is considered: the period for which the incentive form is provided.
The deadline for obtaining the incentive form is the time from the moment the enterprise submits an application (Ta - the application submission term) to the provision of investment resources. It is important that the funds are received on time. The deadline for obtaining the incentive form must not exceed the date for the beginning of the project implementation (Tb). If this condition is not met, then there may be a possibility of non-receipt of funds at the right time, which, in turn, may lead to the suspension of an innovative project.
If the deadline is not met, and the economic entity does not have time, a decision is made to choose another form. If the condition is met, the following criterion is considered: the period for which the incentive form is provided.
The average period for which the form is provided is from 1 to 3 years. Quite a favorable period for business entities, since the average payback period of a company is 2 - 3 years. The main thing is that the period for which the form of incentive is presented (Pp - the period of provision) is less than the payback period (Ppb).
The criterion under consideration is especially important for forms of incentives provided on a refundable basis. If the incentive form is not irrevocable, then all the criteria are passed and the form is received. If it is a repayable basis, it is necessary to take into account the period for which the form of incentive is presented, which should be less than the payback period. In this case, the incentive form will be received on time and for the required period of time.
Conclusion
Taking into account the complexity and peculiarities of conducting innovative activities, business entities, like all enterprises, need support from the state. State support is implemented through a variety of incentive forms, the choice of which is important for the successful implementation of an innovative project. Due to various reasons, in most cases, entrepreneurs are faced with the difficulty of choosing the most suitable of the existing forms that meet all the characteristics and requirements of a particular enterprise. The use of the described criteria will make it possible to choose the most preferable forms of stimulating innovation activity by small and medium-sized enterprises, ensuring the effective implementation of innovative projects.
References
Department of State Target Programs and Capital Investments of the Ministry of Economic Development of the Russian Federation (2020). State Target Development Programs. Retrieved from: https://fcp.economy.gov.ru/cgi-bin/cis/fcp.cgi/Fcp/Title/
Federal law No. 116-FZ (2005). "On special economic zones in the Russian Federation", Retrieved from: http://www.consultant.ru/document/cons_doc_LAW_54599/
Federal Law No. 127-FZ (1996). "On Science and State Scientific and Technical Policy", Retrieved from: http://www.consultant.ru/document/cons_doc_LAW_11507/
Federal law No. 172-FZ (2014). "On strategic planning in the Russian Federation", Retrieved from: http://www.consultant.ru/document/cons_doc_LAW_164841/
Federal law No. 209-FZ (2007). "On the development of small and medium-sized businesses in the Russian Federation", Retrieved from: http://www.consultant.ru/document/cons_doc_LAW_52144/
Galcheva, A. (2020). Helping business and transparency of statistics. JSC "ROSBUSINESSCONSULTING". https://www.rbc.ru/economics/25/05/2020/5ecb8ffd9a79470912b4f29a
Government of the Russian Federation (1999). On a set of measures and the development of state support for small enterprises in the field of material production and the promotion of their innovative activities. Resolution No. 1460. Retrieved on 5 September, 2020, from: http: //www.consultant.ru/document/cons_doc_LAW_25613/92d969e26a4326c5d02fa79b8f9cf4994ee5633b/
Passport of the national project (2018). "Small and Medium Enterprises and Support for Individual Entrepreneurial Initiatives". Retrieved from: http:www.economy.gov.ru/material/directions/nacionalnyy_proekt_maloe_i_srednee_predprinimatelstvo_i_podderzhka_individualnoy_predprinimatelskoy_iniciativy/
Portal of the Innovation Promotion Fund (2020). Regulations and practice guidelines. Retrieved on 5 September 2020 from https://fasie.ru/fund/normativnye-dokumenty/
Resolution (2017). On the forecast of the socio-economic development of the Russian Federation for 2018 and for the planning period of 2019 and 2020, Retrieved from: https://www.economy.gov.ru/material/directions/makroec/prognozy_socialno_ekonomicheskogo_razvitiya/prognoz_socialno_ekonomicheskogo_razvitiya_rossiyskoy_federaciov20_na_2018_ht
Saakyan, A. M. (2014a). Forms of financial incentives for innovative activities of enterprises. Modern concepts of scientific research: materials of the V International scientific and practical conference: Collection of scientific papers. Eurasian Union of Scientists. Economic sciences – Mocow, pp. 145-147.
Saakyan, A. M. (2014b). Tax incentives for enterprises engaged in innovative activities Financial management, 5, 66–74.
Tishchenko, K. (2018). Advantages of investing in the russian innovation sector. https://www.economy.gov.ru/material/file/28388bd7c29291c7ca96f1fe6909c9e3/Skolkovo%20Ventures% 20-% 20Invest% 20in% 20Russia% 20eng% 20vF.pdf
Vlasova, V. V., Kuznetsova, T. E., & Rud, V. A. (2019). Demand for state innovation policy instruments from high-tech enterprises. Institute for Statistical Studies and Economics of Knowledge. National Research University Higher School of Economics. https: //issek.hse.ru/data/2019/07/04/1477949063/NTI_N_134_04072019.pdf
Copyright information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
About this article
Publication Date
01 July 2021
Article Doi
eBook ISBN
978-1-80296-112-6
Publisher
European Publisher
Volume
113
Print ISBN (optional)
-
Edition Number
1st Edition
Pages
1-944
Subjects
Land economy, land planning, rural development, resource management, real estates, agricultural policies
Cite this article as:
Saakyan, A. A. (2021). Stimulation Of Innovative Activities Of Small And Medium Businesses. In D. S. Nardin, O. V. Stepanova, & V. V. Kuznetsova (Eds.), Land Economy and Rural Studies Essentials, vol 113. European Proceedings of Social and Behavioural Sciences (pp. 630-635). European Publisher. https://doi.org/10.15405/epsbs.2021.07.76

