Abstract
The article explores the possibility of the socio-economic public sector's socio-economic system of economy functioning as a self-developing system. The study aims to research the socio-economic system of the economy public sector, its structural elements, and the process of its functioning and establish the prerequisites for this type of system self-development. The study is carried out using the systemic method. The essential features of the socio-economic system are identified. The national economy system components have been analyzed; the problems and the peculiarities of the system functioning in market conditions are identified. The role of the economy public sector as the most crucial producer of public goods and the main economic regulator is revealed. The mission of the socio-economic system of the public sector of the national economy, aimed at sustainable, inclusive economic growth and an increase in the level of social welfare, has been determined. The structural elements of the public sector system have been analyzed. The necessary components of the socio-economic system of the public sector are presented. The basic provisions of the concept of self-development of socio-economic systems are generalized. The conditions for the implementation of such a process are examined. The main features of self-development and self-improvement in the public sector are highlighted. As a result of the study, it was found that the socio-economic public sector's socio-economic system has the ability for self-development.
Keywords:
Introduction
The public sector is an essential component of the socio-economic system of any country's national economy in the world community. The main purpose of such a sector of the economy functioning is to produce high-quality public goods and to provide public services to the population and business, to ensure public safety and to fulfill the obligations of the state, as well as to implement state socio-economic policy and state regulation of the economy. The public sector is the main regulator of the national economy, and its efforts are focused on adjusting the existing market mechanisms and are concentrated on eliminating "market failures", on weakening the crisis manifestations inherent in the socio-economic system and mitigating negative processes taking place in modern society. At the same time, such a sector of the economy closely interacts with the business sector and the households, and its activities have a significant impact on the processes of social reproduction. In modern conditions, the boundaries and scale of activities of the public sector of the economy are determined by the country's government depending on the policy chosen, as well as by the historical features of the particular territory development, by the prevailing national traditions and customs.
Problem Statement
The stability of the entire system of the national economy and the dynamic and sustainable socio-economic development of all spheres of public life is inextricably linked with the activities of the public sector. An efficiently functioning public sector contributes to establishing socio-economic relations between participants in market processes on the most beneficial basis for them, rational state regulation of the national economy system, and the necessary and high-quality public goods production. This fact requires a systematic scientific study. Although in domestic and foreign economic theory, significant attention is not paid to the problem of the effectiveness of the functioning of the socio-economic system of the public sector and its self-development. Therefore, it is important to establish the prospects for the public sector development from the perspective of inclusive (socially-oriented) economic growth and social welfare level increase.
Research Questions
What are the main structural elements and essential components of the socio-economic system of the public sector? Is the socio-economic system of the public sector of the national economy self-developing?
Purpose of the Study
The study aims to research the socio-economic system of the national economy's public sector, analyze its main structural elements, and the process of its functioning directed to public welfare gains. Analysis of the basic provisions of the concept of self-development of socio-economic systems, developed by scientists-economists. Consideration of the socio-economic system of the public sector of the economy from the perspective of self-improvement and based on its self-development signs.
Research Methods
A systematic approach to studying the national economy's public sector is the methodological basis of this scientific research. Our scientific research is carried out using the techniques and methods of dialectical logic, cognition of objective reality, scientific abstraction, and the main provisions of the domestic concept of socio-economic systems self-development.
Findings
A systematic analysis requires a clear “...understanding of what a socio-economic system is as a phenomenon, how it is “arranged” and how it “works”...” (Voskresenskaya, 2017, p. 170). Any socio-economic system forms a single whole, inseparable, has its own specific purpose of functioning in the process of social reproduction and has “... something common and repeating, manifested in a set of features inherent to all complex objects and phenomena:
the system is integral, since the elements included in it are interconnected and unified;
the system is partible and can be subdivided into homogeneous and heterogeneous elements;
the system is multiple, since the state and behavior of any part of it is individual, and a simple set of its constituent parts cannot reveal the general properties of the system” (Tatarkin, 2013, p. 12).
The socio-economic system is a set of interconnected structural elements that stably interact with each other through property relations and the economic mechanism, and its functioning is carried out by processing economic resources into goods and services that satisfy human needs. At the same time, “... an important feature of self-organization of the socio-economic system, by which the general vector of development was recognized and assessed” (Deryabina, 2018, p. 34), a certain spatial structure organization in such a system, which allows us to establish the main directions of systemic development. The socio-economic system includes “... such components as economic agents and their populations, institutions, socio-economic processes in space and time” (Kleiner & Rybachuk, 2019, p. 310). In the process of social reproduction, there is a continuous movement and development of the socio-economic system, which requires research of its functioning and its self-development and self-improvement.
The national economy of any country in the world is also a socio-economic system that includes the business and public sectors, as well as households. It
“…has what is called a mixed economy, where many economic activities are undertaken by private firms, while others are under-taken by the government. In addition, the government alters the behavior of the private sector through a variety of regulations, taxes, and subsidies” (Stiglitz & Rosengard, 2015, p. 4).
The functioning of such a system of the national economy is based on economic relations and on property relations, since all socio-economic processes in modern society are carried out exactly on their basis.
Rather, complex socio-economic processes are taking place in the national economy system, which are largely associated with the aggravation of problems in various spheres of society. Such problems include the presence of crisis phenomena in the socio-economicnational economy's socio-economic system, such as inflation, unemployment, falling production volumes, and labor productivity in many branchers of the real sector. In addition, in many countries of the world there is a slowdown in economic growth, and the systems of their national economies are characterized by financial instability, the presence of negative phenomena and the aggravation of many social problems. Against this background, social unrest is growing, real incomes of the population are decreasing and income differentiation among different social strata is increasing, the socio-economic situation is deteriorating and the level of social welfare is decreasing.
The public sector plays a significant role in any modern national economy (Abramov et al., 2018, p. 37), since it is one of the main elements of such a socio-economic system. T
The public sector in the process of its functioning closely interacts with the business sector and the households, thereby contributing to fairly stable economic relations establishment and development and interrelation among the elements of the socio-economic system of the national economy. At the same time, there is “...a marked change in the role each of them plays in the economic system, an expansion of the range of social policy actors and a significant expansion of the role of business structures in addressing social and economic problems” (Kopytova, 2017, p. 199). This fact is one of the prerequisites for the transformation process of the socio-economic system of the national economy, including the further development of the public sector and its improvement.
There are three main elements in the social and economic system of the public sector of the economy:
state executive and administrative authorities that carry out operational management, financial and economic forecasting and planning, as well as economic regulation of socio-economic phenomena and processes at all levels of management (macro, meso and micro levels) and the implementation of state target programs in accordance with and based on state economic policy developed at a certain stage of social development;
state-owned companies that carry out their financial and economic activities on the basis of state ownership of production means and on a commercial basis in order to replenish the state budget revenues. They cover all priority sectors of the national economy (strategic minerals mining and processing, arms production, space, electricity, transport infrastructure, innovation, etc.);
state institutions and social sphere organizations that produce and provide public goods for the population of the country, as a rule, free of charge, are financed and carry out their activities at the expense of the state budget. Such spheres of state activity include education, medical care, social protection and social transfers allocation, mass culture, libraries, art and folk crafts, sports, environmental safety ensuring in the territory of residence, public infrastructure development, etc.
Therefore, state executive and administrative authorities, so called “public administrative sector”, state-owned enterprises, companies and corporations that represent the “entrepreneurial sector of the state” are the main complex institutional structural elements of the socio-economic system of the public sector; as well as the institutions and the organizations of social sphere, which can be described as the “social sector of the state”.
The socio-economic system of the public sector of the economy is characterized by the presence of state ownership of the main production means and financial resources of the state as the basis for its functioning, organizational and legal forms of state activity, economic relations and close correlation among the structural elements of the public sector, the economic mechanism. Wherein “…combination of parameters… determines the type and individuality of socio-economic systems” (Treshchevsky et al., 2018, p. 24).
Figure
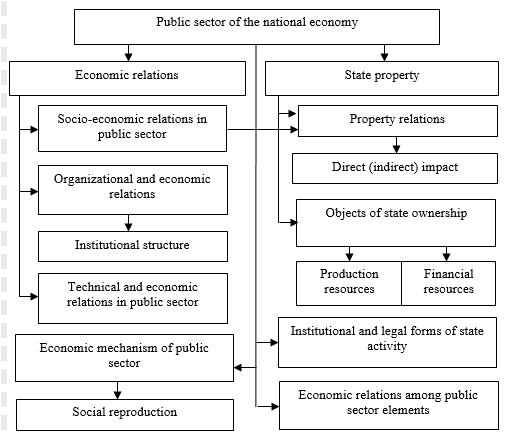
Let us consider in details the basic components of the socio-economic system of the public sector, shown in Figure
State ownership is all types of property that belongs to the state in whole or in part, for example, is in joint ownership. At the same time, it includes not only state owned land, fixed and working capital owned, used and at the disposal of state-owned companies, but also funds from the state budget, various funds and reserves created by the state, etc.
Economic relations in the public sector are characterized by certain interrelationships that economic actors enter into in the process of social reproduction. Such relations are subdivided into socio-economic, organizational-economic and technical-economic. At the same time, organizational and economic relations cover the institutional structure of the public sector. State institutions “... perform ... functions of economic and social regulation that are important for determining trends in the spatial development of the economy” (Buchwald, 2019, p. 123).
The organizational and legal form of state activity means the legal status of each economic entity in the public sector, enshrined in law. For example, a government enterprise, a state unitary enterprise, a state corporation, a joint stock company, a budgetary institution, etc.
Economic relations between the elements of the public sector form the patterns of the socio-economic system functioning, provide for the system stability and integrity preservation, and ensure “... stable economic growth at high rates” (Ershov et al., 2019, p. 20). At the same time, there is both horizontal and vertical relationships between the public sector elements. In the first case, they reflect the relationship between economic entity in the public sector, which are not subordinate to each other and are at the same hierarchical level. In the second case, there is the subordination of one economic entity to another, which is at a higher hierarchical level.
A certain set of tools, methods, legal norms, forms and methods of state activities organization, including the process of public goods production and state regulation of the economy, are considered as the economic mechanism of the state sector of the economy. Forms of state regulation must have sufficient flexibility in accordance not only with general aims of social policy but also with local features and needs of regions` population (Shabunova & Kosygina, 2019, p. 88). The economic mechanism aims not only to increase the efficiency of the public sector, but also to develop dynamically the entire system of the national economy, to improve the process of social reproduction.
The above-mentioned components of the socio-economic system of the public sector of the national economy characterize its integrity, independence and reflect specific features.
The issues of the functioning and self-development of socio-economic systems were the subject of the scientific works of leading Russian scientists, and first of all, of academician Tatarkin, who developed the concept of self-development of socio-economic systems. This concept, in fact, is the basic provision on the spatial organization of the entire system of the national economy. Proving his concept, Tatarkin (2013) argued that “...the system is integral…the system is divisible…the system is multiple...” (p. 12). These main features of the socio-economic system allowed Tatarkin to draw conclusions about the ability of a certain territory for further self-development and self-improvement. He singled out and considered two basic conditions for the self-development of any socio-economic system, namely “internal self-sufficiency” and “favorable external conditions”. Tatarkin (2013) claimed:
The self-development of...economic systems...presupposes two system-forming conditions. I. the internal self-sufficiency of ... the system, capable of maintaining its organizational integrity and ensuring the long-term sustainability of...development... II. Favorable external conditions (external environment), which in their entirety ensure a stable balanced self-development...of socio-economic systems in the strategic perspective (p.p. 12-13).
According to Tatarkin, the first and main condition for self-development and self-improvement of the socio-economic system that is part of the national economy “... characterizes the availability of its own resources and the possibility of their optimal use, and the second is the need to create an appropriate institutional environment that ensures sustainable self-development ... in a strategic perspective” (Sergeev, 2017, p. 44).
The concept proposed by Tatarkin, can be applied to the socio-economic system of the state sector of the national economy, which is not stable functioning and sustainable, but has the ability to improve and develop. All reproduction processes also take place in the public sector, namely, production, distribution, exchange and consumption. The state sector of the economy owns, disposes and uses state ownership of the production means, as well as budgetary resources to fulfill the mission assigned to it, the goals set and the functions established by the state. At the same time, the public sector system is constantly in motion, develops cyclically, and periodically undergoes transformational change processes. The scale of functioning and the types of activities, the forms of state ownership, as well as the institutional boundaries of the state sector of the national economy are subject to constant transformations under the influence of privatization or nationalization processes, the use of new methods of state regulation of the economy, innovations, changes in proportions in the public goods production provided to the population, etc. The vector of state socio-economic policy may also change significantly, since "...in different states of the economy, one needs its own instruments of macroeconomic policy, as well as an idea of the limits of its applicability..." (Burenin, 2019, p. 80). Exactly these circumstances indicate the features of a self-developing socio-economic system.
Socio-economic system of the public sector of the national economy has the ability to self-development and self-improvement, since such a system has all the features and properties of a self-developing system, which include:
- has state ownership of the means of production, uses material and labor resources in the course of its activities, and also manages the financial resources of the state in the form of the state budget and state non-budgetary funds, as well as various funds for socio-economic development,
- the presence of stable socio-economic relations and sustainable relationships between all elements of the public sector of the national economy, namely, state executive and administrative authorities, public corporations and the state social sector, as well as business sector and households;
- an economic mechanism that ensures not only the uninterrupted functioning of the institutional structures of the state sector of the national economy itself, but also aimed at expanded social reproduction, as well as sustainable economic growth, improving the quality of life of the population and social welfare.
The public sector is the financial and property basis of any country, and its activities are associated with the production of quality public goods and services, and aims at effective government regulation of the entire socio-economic system of the national economy. However,
... in this sector that part of society is concentrated, the lack of income or excessive expenditures of which does not allow it to become an independent market participant, dooming it to dependence on the share of the budget allocated to it (Mamedov, 2018, p. 12).
But, at the same time, the state sector of the national economy, nevertheless, has the ability to ensure the process of expanded reproduction by mobilizing available resources in the public interest. In addition, the public sector can quickly respond to crisis phenomena occurring in the entire system of the national economy and to negative processes occurring in the life of modern society.
Conclusion
Thus, the public sector of the economy is a complex, independent and rather specific socio-economic system as part of the national economy, which has all the main features of a self-developing system. The main functions of the public sector are the public goods production and state regulation of the economy, aimed at the stability of the entire socio-economic system of the national economy, creating the preconditions for sustainable inclusive economic growth and increasing the level of social welfare. State executive and administrative authorities, state-owned companies, government agencies and social organizations are identified as the elements of the public sector structure. The public sector contributes to the establishment of stable ties and the development of economic relations in the socio-economic system of the national economy, namely, between the state, business sector and households.
Reproduction processes take place in the socio-economic system of the public sector, like in any other self-developing system. Such a system is characterized by the presence of state property, economic relations and close relationships between its structural elements, the economic mechanism, which indicates the integrity of such a system, its independence and functional specifics. The socio-economic system of the public sector of the economy is not stable functioning and sustainable. In the course of its functioning, such a system is periodically subject to changes, since its scale and institutional boundaries, types of activities and forms of state ownership have the ability to transform when the conditions of socio-economic development change. All these features point to a self-developing socio-economic system of the public sector of the economy, which has the ability to develop and improve itself.
References
- Abramov, А. Е., Aksenov, И. V., Radygin, А. D., & Chernova, М. I. (2018). Sovremennyye podkhody k izmereniyu gosudarstvennogo sektora: metodologiya i empirika [Modern approaches to public sector measuring: methodology and empirics]. Economic policy, 13(1), 36-69.
- Buchwald, Е. М. (2019). Institutsional'nyye problemy strategirovaniya prostranstvennogo razvitiya v Rossii [Institutional problems of spatial development strategies in Russia]. Journal of the New economic Association, 2(42), 121-136.
- Burenin, А. N. (2019). Predely makroekonomicheskoy politiki pod uglom zreniya ekonomicheskikh krizisov [The limits of macroeconomics policy from the viewpoint of economic Crises]. Economic policy, 14(1), 76-91.
- Buzgalin, А. V., & Kolganov, А. I. (2016). Politicheskaya ekonomiya i ekonomicheskaya politika. Rynok. Kapital. Obshchestvo [Political economy and economic policy. Market. Capital. Society]. Terra Economicus, 14(1), 27-47.
- Deryabina, М. А. (2018). Metodologicheskiye osnovaniya issledovaniya mezourovnya ekonomiki kak slozhnoy sistemy [Methodological foundations of the economy meso level study as a complex system]. Journal of institutional studies, 10(3), 30-39.
- Ershov, М. V., Tanasova, А. S., & Sokolova, Е. Y. (2019). O nekotorykh podkhodakh gosudarstvennogo upravleniya dlya stimulirovaniya ekonomicheskogo rosta [On some approaches of public administration to stimulating economic growth]. The Manager, 10(5), 20-32.
- Kleiner, G. B., & Rybachuk, М. А. (2019). Sistemnaya sbalansirovannost' ekonomiki Rossii. Regional'nyy razrez [System Balance of the Russian Economy: Regional Perspective]. Economy of region, 15(2), 309-323.
- Kopytova, E. D. (2017). Revisiting the development of cooperation between the state, business, and society in addressing territorial development issues. Economic and Social Changes: Facts, Trends, Forecast, 10(5), 197-215.
- Mamedov, О. Y. (2018). Nerynochnyy drayver smeshannoy ekonomiki [The Non-market driver of a mixed economy]. Terra Economicus, 16(1), 6-19.
- Sergeev, А. М. (2017). Kriterii i usloviya samorazvitiya territorial'nykh sistem [Criteria and conditions for the self-development of territorial systems]. Journal of economic theory, 3, 40-46.
- Shabunova, A. A., & Kosygina, K. E. (2019). Public administration issues in the development of the non-profit sector at the regional level. Economic and Social Changes: Facts, Trends, Forecast, 12(4), 86-103.
- Stiglitz, J. E., & Rosengard, J. K. (2015). Economics of the public sector. new york, London: W.W. Norton & Company.
- Tatarkin, А. I. (2013). Samorazvitiye territorial'nykh sotsial'no-ekonomicheskikh sistem kak potrebnost' federativnogo obustroystva Rossii [Self-development of territorial socio-economic systems as a need for the federal arrangement of Russia]. Economy of region, 4(36), 9-26.
- Treshchevsky, Yu. I., Risin, I. E., Korobeynikova, L. S., & Gavrilov, V. V. (2018). Management of Changes of Socio-economic Systems: Economic Analysis of the State and Consequences of the Systemic Feature. Studies in Systems, Decision and Control, 135, 21-30.
- Voskresenskaya, N. О. (2017). Ekonomicheskaya komparativistika kak nauka i uchebnaya distsiplina: (O knige R. M. Nureyeva “Sravnitel'nyy analiz ekonomicheskikh sistem”) [Comparative economics as a science and academic discipline: (about R. M. Nureyev’s book “Comparative Analysis of Economic Systems”]. Journal of institutional studies, 9(3), 164-180.
Copyright information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
About this article
Publication Date
16 April 2021
Article Doi
eBook ISBN
978-1-80296-104-1
Publisher
European Publisher
Volume
105
Print ISBN (optional)
-
Edition Number
1st Edition
Pages
1-1250
Subjects
Sustainable Development, Socio-Economic Systems, Competitiveness, Economy of Region, Human Development
Cite this article as:
Gersonskaya, I. (2021). The Public Sector As A Self-Developing Socio-Economic System. In E. Popov, V. Barkhatov, V. D. Pham, & D. Pletnev (Eds.), Competitiveness and the Development of Socio-Economic Systems, vol 105. European Proceedings of Social and Behavioural Sciences (pp. 448-456). European Publisher. https://doi.org/10.15405/epsbs.2021.04.49

