Abstract
This article describes the preparation of a future teacher’s master’s degree, capable of carrying out specialized foreign language (FL) teaching in various types of educational organizations. The introduction of specialized foreign language teaching for schoolchildren greatly enhances students' ability to independently choose their future educational and professional path, since knowledge of a FL contributes to the communication skills development tolerance, the professional mobility growth. The urgency of this problem is due to the insufficient the methodology development for the university’s future teacher training. The future teacher is engaged in the field of specialized foreign language education to overcome the lack of educational programs for specialized education implemented in the system of higher education. The article presents the main pedagogical conditions for educational process functioning in the magistracy aimed at preparing the future FL teacher of a profile school: the professionally oriented intention of studying FL students; updating and accounting of knowledge of professionally directed FL content; independent choice of an individual educational route by the undergraduate; creative implementation in teaching. The article describes the content of the master’s program “Foreign language education in the system of core training” and verifies its effectiveness, the criteria for a graduate’s readiness for future professional activity in the field of core education (motivational, cognitive, technological, personal), the results of experimental work confirming the effectiveness of pedagogical conditions of formation of readiness of a undergraduate university to the implementation of specialized teaching of a foreign language.
Keywords: Masterprofile trainingforeign language (FL)readiness
Introduction
In modern conditions, the education system should not only teach, giving ready-made knowledge, but also form students' desire to master new knowledge and create opportunities for their further professional growth. The solution the professional development problem of a future specialist, taking into account the real needs of the labor market, is seen in the introduction of specialized training. Under the profile training in a broad sense, we understand the system of organization of education of schoolchildren, in which the training of high school students passes through various programs with the predominance of certain subjects. Modern education needs updating, it is necessary for modern pupil to be given a wide choice: an educational program, the curriculum, an educational route, a training profile. And so, for today profile training is one of priority directions of updating of modern education, achievement of new quality" (Konakbeyeva, Zholdasbekova, & Erdogan, 2014). Broadly speaking, we understand "the system of the organization of secondary education at which training takes place in the senior classes according to different programs (profiles) with prevalence of these or those objects" as profile training (Korotkova, 2007).
The long experience of the Russian school in using the model of differentiated education allows us to state that specialized education has its advantages and disadvantages. However, it is indisputable that with the introduction of the profiling of high school students, their ability to independently choose their future educational path significantly increases (Milovanova, 2006).
Currently, there are significant changes in the geopolitical and socio-economic life, causing the need for significant changes in the education system. These changes include raising the status of a FL. Knowledge of a foreign language is an urgent need for Europeans of the XXI century. It contributes to the formation of modern thinking in the younger generation, the development of communication skills and tolerance, the growth of professional mobility.
An analysis of the current state of FL teaching in various educational institutions of the country has revealed a number of problems, in particular, the lack of conceptual understanding of the principles and mechanisms for the implementation of specialized foreign language education at its various stages. There is not enough research on the methodology of vocational training of a future teacher of a foreign language who will work in the context of continuous foreign language education, providing foreign language education from preschool age (“so-called early education”) and ending with distance learning, aimed at self-learning of students in the framework of different learning profiles. In our opinion, in order to solve this problem, it is necessary to introduce new master programs for the training of pedagogical personnel, capable of carrying out specialized foreign language training.
Problem Statement
An analysis of the current state of foreign language teaching in various educational institutions of the country has revealed a number of problems, in particular, the lack of conceptual understanding of the principles and mechanisms for the implementation of specialized foreign language education at its various stages. There is not enough research on the methodology of vocational training of a future teacher of a foreign language who will work in the context of continuous foreign language education, providing foreign language education from preschool age (“so-called early education”) and ending with distance learning, aimed at self-learning of students in the framework of different learning profiles. In our opinion, in order to solve this problem, it is necessary to introduce new master programs for the training of pedagogical personnel, capable of carrying out specialized foreign language training.
“The need to introduce profile differentiation at all levels of school education” was updated by domestic methodologists in 1988 in the “Concept of general secondary education” developed by them. In subsequent regulatory documents (“Concept of modernization of Russian education for the period up to 2010”, “Concept of specialized education”) this idea was developed and concretized (Kuznetsov, Pinsky, Ryzhakov, & Filatova, 2004, p. 3).
Currently, the profiling of education affects all regions of the Russian Federation. The Ministry of Education and Science of the Russian Federation recommends the following teaching profiles in high school: humanitarian, natural-mathematical, socio-economic, information-technological (Chistyakovа, 2002, p. 3). Moreover, each profile involves the study of basic general education disciplines, subjects that determine the direction of the profile, and elective courses.
With specialized training, the number of non-core items is necessarily reduced. The basic, specialized and elective courses introduced into the educational space of schools according to the Special Education Concept are correlated in a ratio of 50:30:20 (Takhtamysheva, 2006). The basic general educational subjects include mathematics, history, Russian language, physical education and a foreign language.
Research Questions
It should be noted that the last several years the researches in the field of profile education became more active. The problems connected with the introduction of the general education of profile training at the senior step are considered in works of Akulovа (2006), Artemova (2003a), Artyukhova (2003), Boguslavsky (2009), Chistyakova (2002), Korotkova (2007), Lentell (1994), Vaisburd (2000) etc.
The greatest fame was gained by the projects of profile training developed on many questions. They are the following: management of profile training of seniors (Afanasyevа & Nemovа, 2005), the creation of regional programs of the development of profile training, the ways of the organization of professional development and retraining of personnel for profile school (Kasprzhak, 2004). Modeling of educational programs for schools with profound studying of separate objects (Kolesnikov, 2006; Vaisburd, 2000) is of great interest too. The specific features of the contents and the process of training at profile school (Bessonov & Okolelov, 2006) are also important.
Arefyev (2003), Artemova (2003b), Flowerdew (1993) studied the development of professional and pedagogical competence of the teachers of the system of profile training. Lerner (2004)investigated the role of elective courses in profile training; Konakbeyeva, Zholdasbekova, and Erdogan (2014) developed the theory and the practice of the organization of profile teaching; Kuznetsov, Pinsky, Ryzhakov, and Filatova (2004), studied the continuity of training at school and at a higher education institution as new opportunities of profile training, Afanasyeva and Nemova (2005)s tudied planning of teaching and educational process in the system of profile training.
Purpose of the Study
The analysis of periodicals and special literature shows that the nature and content of profile training demand further development. Today the theoretical-scientific development of a problem of forming the future teacher’s readiness of a foreign language for the organization of profile training, search of the ways defining the efficiency of this teaching is necessary. It is necessary to develop a model of the didactic system of forming the future teacher’s readiness of a foreign language for the organization of profile training, to formulate the main conditions, principles and approaches of this teaching.
The modern profile school demands a teacher with a certain level of professionalism including motivational, informative and technological components, the results of educational activity (knowledge and skills), the system of valuable orientations.
We assumed that training of a future teacher for the organization of profile training in a foreign language will be effective if:
training is realized in the conditions of specially developed master program;
students’ knowledge of specifics of profile foreign language training is actualized in the course of training;
the principle of an intensification of professionally focused training in a foreign language of undergraduates is implemented;
the realization of basic provisions of competence-based approach is enabled.
We have set the following tasks:
to design content of the experimental program directed to formation of readiness of undergraduates - future teachers to the organization and implementation of profile training in a foreign language;
to define criteria for evaluation of readiness of undergraduates for future professional activity; to make an experiment on approbation of the master program; to analyze results of the carried-out experimental work.
Research Methods
The methodological basis of a research was made by the philosophical and psychological ideas of development of the personality in education, by the pedagogical bases of the theory and a technique of professional pedagogical education.
We applied a complex of methods: analysis of theoretical sources and pedagogical experience and their synthesis, pedagogical observation, questioning and introspection of students, method of expert evaluations.
We recognized that the undergraduate is a subject of both future professional activity and educational process in a magistracy (Kolesnikov, 2006). Master preparation has to create conditions for development in future teachers of a foreign language of readiness for professional activity, direct students to mastering professional competences, motivate them on acquaintance with the best examples of professional skill. Just competence-based approach to process of training of masters as future teachers of a foreign language in various profile educational institutions is also aimed at it. From a position of this approach educational process in a magistracy has to be personal focused, have the most independent character, have a research focus.
Today the profiling of training affects all regions of the Russian Federation. The Ministry of Education and Science of the Russian Federation recommended the following set of profiles in high school: humanitarian, natural and mathematical, social and economic, information and technological. At the same time each profile assumes studying of basic general education disciplines, the objects defining the direction of a profile, and elective courses.
At profile training the quantity of not specialist subjects is compulsorily reduced. The schools entered into educational space basic, profile and elective courses according to the Concept of profile training correspond in a proportion 50:30:20. Mathematics, History, Russian, Physical Education and Foreign Language are among basic general educational subjects.
Findings
In a basis of design of contents of the curriculum of the master program we put the idea of the competence-based approach about training constructed taking into account need of the student to independent development of knowledge. The main objective of training of the master is the formation at students of readiness to creatively master new ways of pedagogical activity in the sphere of foreign-language education.
Within competence-based approach we developed basic provisions of functioning of the educational process in a magistracy directed to training of a future foreign language teacher of profile school:
Professionally focused intension of studying by students of a foreign language (depending on a profile of school of the future of the teacher): humanitarian, natural-science, special, focused on a concrete profession.
Updating and the accounting of knowledge by students of professionally directed foreign-language content.
Independent choice by the undergraduate of an individual educational route.
Creative realization of undergraduates in pedagogical activity.
In 2012 at our university the master program for the direction of preparation 44.04.01 Pedagogical education an orientation (profile) "Foreign-language education in the system of profile preparation" was developed.
It is known that the concept "foreign-language education" is introduced for scientific use by the methodologist E.I. Passov in the late nineties of the XX century. Now the given term became standard among teachers of a foreign language. By Passov's (2000) definition, "foreign-language education - completely organized pedagogical process directed to training and education of pupils by the contents and means of a foreign language making positive impact on their cultural enrichment and creative development" (p. 28). Foreign-language education in modern society has to create conditions for formation of communicatively focused personality capable to cross-cultural communication in various spheres of human activity: scientific, productive and economic, socio-political, cultural and scientific and educational.
The graduate who mastered the program of a magistracy has to be able to work in various types of profile foreign-language education.
Today scientists allocate the following types of profile foreign-language education: pre-school, school, philological, not philological (Schukin, 2004, p. 56).
Initial link in modern system of profile foreign-language educational institutions in our country is the pre-school foreign-language education covering children of pre-school age.
School foreign-language education has three steps. The first step of training is elementary school (2-4 classes), the second step of training is the main, basic school (5-9 classes), the third step is profile school (10-11 classes).
Today the purpose of profile school of foreign-language education is achievement of the level of development of foreign-language communicative competence which comes nearer to the B2 level in terms of the Council of Europe. The learning of foreign language can be organized by means of a language and special course when studying humanitarian and natural-science disciplines, and also the disciplines focused on a concrete profession.
The pupil’s choice of future profession influences his specialization of studying of a language. It can be as intention to learn a foreign language in special higher education institution, and desire to study other subject domain by means of a foreign language. A foreign language can be used also in practical activities of a future expert, for example, as the guide-interpreter, the administrative assistant with knowledge of a foreign language, etc. (Bim, 2003).
"As a profile subject the foreign language is in the standard plan of a philological profile. At the expense of enough class periods (6 hours a week on the first foreign language) this standard plan creates conditions under which becomes possible to provide profound studying of a subject and its profile (philological) orientation" (Bim, 2007, p. 96).
If to follow classification of profiles of the system of foreign-language education, then it is possible to allocate still a course profile. Courses have various duration of training and are focused on various level of training of pupils.
The distance learning is allocated as the last link in this system of foreign-language education providing independent studying of training courses by pupils.
The higher school allocates a philological and not philological profile. Training in a foreign language in philological higher education institution is carried out within the "Linguistics and Cross-cultural Communication" direction. Classes in a foreign language in not philological higher education institution focus the student on language acquisition as the means of communication within the specialty elected by him. At the same time as a source of information the specialist subject teacher's lectures along with the educational, adapted and authentic popular scientific texts adapted by works of fiction and newspaper reports of social and political and sociocultural contents, etc. are used.
Developing content of the master program, we considered this classification. Therefore, the contents of the curriculum included such disciplines as "Early foreign-language education: traditions and innovations"; "The professional focused training in a foreign language in technical lyceum (college)"; "A foreign language in the sphere of business, tourism and management"; "A business foreign language"; "A foreign language in the sphere of law"; "Translation bases in the professional sphere", etc.
It should be noted that "the profiling at profile training in a foreign language occurs due to more careful study of an invariant kernel of content of training; connections of modules with the additional profile focused material (corresponding to a professional orientation of a profile); attraction of elective courses and practician" (Bim, 2004, p. 9).
The graduate who mastered the program of a magistracy has to have professional competences, in particular, ability to apply modern techniques and technologies of the organization of educational activities, diagnostics and estimation of quality of educational process for a foreign language according to various educational programs. At it ability to form the educational environment and to use professional knowledge and abilities in realization of problems of innovative policy in the field of foreign-language education has to be developed; and also readiness for development of new ways and methods of training, for the analysis of results of process of their use in the profile educational organizations is created.
According to requirements of federal state educational standard for the direction of preparation 44.04.01 Pedagogical education students when forming the individual educational program have the right within the volume of the school hours allowed for development of disciplines for choice to choose concrete disciplines. As disciplines for choice cover a considerable range of methodical and pedagogical areas, students get advice at the choice of disciplines, to their influence on future vocational training. The leading departments of institute of philology provided an alternative of disciplines for choice in each cycle as a part of several disciplines.
The contents of the master program "Foreign-language Education in System of Profile Preparation" included elective courses and open classrooms: "Technology of testing in domestic didactics", "Training of preschool children for cross-cultural communication", "Teaching a foreign language in the context of global education", "Current trends of foreign-language education in domestic and foreign didactics", "Mnemonics as way of a learning of foreign languages", etc.
In the curriculum of training of a future foreign-language education master competence-based approach is fully realized. It finds reflection in the following:
the requirement to results of development of the main educational program in the system of common cultural, professional competences is detailed in ranges of competences of educational modules, subject matters, pedagogical, scientific and pedagogical and research practical training, final state assessment;
it is established in working programs of subject matters, practical trainings that there is compliance of the formed competences and content of educational activity of students;
there are basic descriptors in each competence as means of formation and diagnosing in the maintenance of a subject matter;
in planning of studies on the maintenance of a concrete subject process of formation of competences through kinds of activity, through carrying out forms, through contents and means of activity is designed;
the content of an intermediate and final assessment is determined by the procedure of measurement of formation of certain competences.
A special role in educational process is played by the organization of rational research activity of undergraduates(Hutchinson & Waters 1987, p. 145). Research activity includes research work in a semester, a scientific seminar, practice, preparation of final qualification work and its protection on a State Final Examination. The subjects of researches chosen by undergraduates are in the course of the strategic direction of development of modern foreign-language education. Urgent problems of a domestic and foreign technique of training in foreign languages at all stages of profile foreign-language education act as a subject of researches.
The major stage in system of training of future master are control and an assessment. On protection of final qualification works the results of two years' training of undergraduates - future experts in system of profile foreign-language education are summed up. The analysis of final qualification works of undergraduates of the last years of release showed that the new theoretical bases and practical decisions for optimization of process of profile training in a foreign language are revealed.
The main educational program of training of masters of foreign-language education in system of profile preparation is annually updated according to the level of development of science, culture, economy, the social sphere, changes are made to working programs of disciplines for the main and additional literature.
Criteria for evaluation of preparation for future professional activity of the undergraduate
We marked out the following criteria for evaluation of preparation for future professional activity of the undergraduate:
Valuable-cognitive, allowing to define existence of a professional orientation and the need for creative pedagogical activity of the undergraduate, shown in foreign-language literacy, possession of knowledge of the theory and practice of profile foreign-language education.
Operational, shown in ability to enable development and the realization of techniques, technologies and methods of training in a foreign language, the analysis of results of process of their use in the profile educational organizations.
Reflexive, the personal criterion allowing to determine the personal growth of the student in the course of his vocational training (change in the identity of the undergraduate, his relations in system teachers-students-students; student-pupils-teacher).
Experimental Work
In the course of experimental work there was an introduction and check of efficiency of the developed experimental program, results of a pedagogical experiment were carefully traced. The experimental program of forming readiness of the undergraduate of the university for implementation of profile training in a foreign language reflects integrity, systematicity, regularity and phasing of this process; provides the personal and professional growth, development of research qualities; assumes obligatory performance of a number of the organizational and pedagogical conditions providing transition to higher level of formation of the called readiness:
the creation of a didactic environment in the foreign language lessons that stimulates motivation for the implementation of profile teaching in a foreign language;
the organization of classroom and out-of-class practice of masters in profile training in a foreign language;
development of analytical and reflective master's skills.
The content of the stating stage of the experimental work was the study of the peculiarities of the existing practice of forming the readiness of the master student of the university for the implementation of profile training in a foreign language. The organization and realization of this stage of an experiment were carried out in the following directions: assessment of completeness of ideas of students of specifics of readiness for implementation of profile training in a foreign language; disclosure of nature of the difficulties experienced by them in the course of profile training in a foreign language; studying the extent to which students are interested in formation of readiness of the undergraduate of the university for implementation of profile training in a foreign language; determination of initial level of the called readiness.
In the course of the forming experiment the maintenance of each stage of formation of readiness of the undergraduate of the university for implementation of profile training in a foreign language was defined, the efficiency of the developed experimental program is experimentally checked. Problems of the forming and control stages of skilled and experimental work consisted in approbation of efficiency of organizational and pedagogical conditions of formation of readiness of the undergraduate of the university for implementation of profile training in a foreign language; in determination of number of students of the experimental and control groups having low, average and high levels of the called readiness. In the process of the analytical-generalizing stage there was a judgment and interpretation of quantitative and qualitative data of experimental work on formation of readiness of the undergraduate of the university for implementation of profile training in a foreign language.
In the process of experimental work, the following stages of the formation of this competence were identified: adaptive, technological, creative and reflective.
In the course of an adaptation stage of formation of readiness of the undergraduate of the university for implementation of profile training in a foreign language there was an awareness of the importance of this activity by students; mastering the ability to collect and classify information, to independently use reference books; to find intersubject communications; the possibility of use of domestic and foreign experience, etc. was fixed. Students were offered such forms of work as, for example, commenting on statements and writing essays on profile education, brainstorming: "Why is a foreign language necessary?", a press conference: "10 years later", trainings.
The feature of a technological stage is the active use of innovative educational technologies by students not only in the process of studying a foreign language, but also in the course of educational, research and production practices. This stage is characterized by further mastery of the students of the profile thesaurus, awareness of intralinguistic regularities of a target language, development of logical and critical thinking, ability to perform project work, to prepare a presentation, an abstract, a presentation, a report or an article, etc. They learn to correct personal development of pupils by means of a foreign language, methodically and competently plan and conduct a lesson of a foreign language in profile classes, an out-of-class activity.
At a creative and reflexive stage students have the developed pedagogical imagination; are capable of seeing arising problems and contradictions; it is productive to work in an unusual situation of teaching and educational process; to predict, analyze and estimate efficiency of use of various methods and technologies of training in a foreign language; to expect consequences and effectiveness of foreign-language activity; to derive benefit from experience; to self-improve in professional and personal aspects. Activity of masters at this stage is characterized by high degree of independence, the teacher acts as an adviser, directing and correcting methodical search, research activity of students.
Results of the carried-out experimental work
Results of comparative diagnostics of formation of readiness of a university undergraduate student for implementation of profile training in a foreign language at the stating and final stages of experimental work in accordance with the criteria we have singled out are presented in the table and diagram. In the experimental group (EG) 25 students, took part in the control group (CG) – 27 students.
The comparative analysis shows positive dynamics of the criteria of formation of readiness of the undergraduate of the university for implementation of profile training in a foreign language recorded in experimental and control groups of bachelors at the stating and control stages of skilled pilot study. Figure
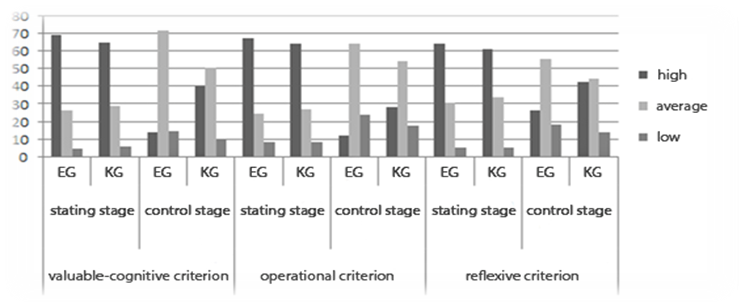
The existence of a professional orientation became clear by means of the question "What Motives of Your Choice of Profession of the Teacher of a Foreign Language?" questioning of undergraduates of the second year regarding identification of a professional orientation showed that most of students fix the fair idea of specifics of the chosen profession. It is caused, first of all, by professional interest in the chosen profession at all interviewed, the conscious choice of a pedagogical profession (100%). It is dictated by desire to carry on pedagogical family traditions (17%), the aspiration to devote itself to this noble profession (38%), desire to impart the knowledge to children, to train them (44%), desire to eradicate cruelty, bad manners of people (2%).
For an examination, abilities and level of the acquired competences observation of work of students on a practical training on a foreign language and a technique of its teaching was made, and also during student teaching. An indicator of mastering special knowledge of the theory and practice of profile training in a foreign language is results of examinations. The percent of quality of knowledge made 97%, progress of-100%.
The interview with graduates of a magistracy showed that undergraduates in the majority of the required parameters are satisfied with quality of services of higher education institution. 98% interviewed on the expert's question "Training in this direction of preparation satisfies you" - answered in the affirmative. Quality of knowledge of the studied disciplines conforms to requirements of the federal standard, the contents of master theses meet the requirements of professional kinds of activity. The State Examination Board recognized high the level of scientific and practical training of graduates for professional kinds of activity.
Thus, the data of skilled and experimental work confirm efficiency of the developed program and organizational and pedagogical conditions of formation of readiness of the undergraduate of the university for implementation of profile training in a foreign language, indicate a pronounced positive dynamics of criteria of formation of the called readiness in experimental group.
Conclusion
The complex of the held events during implementation of the master program allows to draw to the following conclusions:
The developed master program conforms to requirements of federal state educational standard for the direction of preparation Pedagogical education.
The system of the organization of the educational program is focused on a methodological support and psychology and pedagogical support of orientation of students to the purposes and problems of profile foreign-language education. Immersion in the chosen route of an educational trajectory gives the chance to students to estimate correctness of purposes.
The educational environment created in higher education institution is directed to identification, support and realization of personal potential of students, strengthening of their motivation on mastering a complex of common cultural, all-professional and professional competences.
The received results of development by students of the master program confirm her main idea – increase in professional level of students - future teachers of a foreign language in profile educational institutions.
The master of foreign-language education is the widely erudite teacher capable to independently solve research, educational and educational problems. The close integration of educational, research, scientific and practical and scientific and pedagogical preparation provided by the Federal state VO educational standard allows to prepare the masters owning all necessary competences, complex professional challenges, capable to the decision.
As practice shows, our graduates of a magistracy are demanded by educational bodies in labor market.
References
- Afanasyeva, T. P., & Nemova, N. V. (2005). Profil'noe obuchenie: pedagogicheskaya sistema i upravlenie. Kniga 2. Sistema profil'nogo obucheniya starsheklassnikov[Profile training: pedagogical system and management. Book 2. The system of specialized education for high school students]. Moscow: APK i PPRO.
- Akulovа, O. V. (2006). Informacionnaya rabota v usloviyah profil'nogo obucheniya [Information work in conditions of profile training]. Moscow: Caro.
- Arefyev, I. P. (2003). Podgotovka uchitelya k profil'nomu obucheniyu starsheklassnikov [Training teachers to profile training of students]. Pedagogika, 5, 49-55.
- Artemova, L. K. (2003a). Profil' obucheniya diktuet regional'nyj rynok truda [Learning profile dictates regional labor market]. Narodnoe obrazovanie, 4, 84-88.
- Artemova, L. K. (2003b). Profil'noe obuchenie: opyt, problemy, puti resheniya ["Special education": experience, problems, solutions]. Ped. obrazovanie i nauka, 4, 22-31.
- Artyukhova, I. S. (2003). Problema vybora profilya obucheniya v vuze [The problem of choosing the profile of training in high school]. Pedagogika, 2, 28-33.
- Bessonov, R. V., & Okolelov, O. P. (2006). Specifika obucheniya v profil'noj shkole: soderzhanie i process [Specifics of training at profile school: maintenance and process]. Pedagogika, 7, 23-29.
- Bim, I. L. (2003). Rekomendacii po organizacii predprofil'noj podgotovki shkol'nikov s orientaciej na filologicheskij profil': inostrannye yazyki [Recommendations about the organization of preprofile training of school students with orientation to a philological profile: foreign languages]. Inostrannyie yazyiki v shkole, 6, 2-7.
- Bim, I. L. (2004). K probleme profil'nogo obucheniya inostrannym yazykam na starshej stupeni polnoj srednej shkoly [To a problem of profile training in foreign languages at the senior step of full high school]. Inostrannyieyazyikivshkole, 6, 8-14.
- Bim, I. L. (2007). Profil'noe obuchenie na inostrannyh yazykah na starshej stupeni obscheobrazovatel'noj shkoly. Problemy i perspektivy: izuchenie [Profile training in foreign languages at the senior step of comprehensive school. Problems and prospects: studies]. M.: Obrazovanie.
- Boguslavsky, M. V. (2009). Istoriya otechestvennoj pedagogiki XX veka: edinstvo nepreryvnosti i diskretnosti [History of Russian pedagogy of the twentieth century: the unity of continuity and discontinuity]. Pedagogika, 6, 84-96.
- Chistyakovа, S. (2002). Nado vybrat' zadachu tak, chtoby vybor ostalsya za det'mi. Profil'noe obrazovanie: vzaimodejstvie protivopolozhnostej [Need to choose the tasks, so that the choice remained with children: education: the interaction of opposites]. Pervoe sentyabrya, 41, 3.
- Flowerdew, J. (1993). An educational, or process, approach to the teaching of professional genres ELT Journal, 47/4, 305-316.
- Federal'naya programma razvitiya obrazovaniya; Koncepciya modernizacii rossijskogo obrazovaniya na period do 2010 goda; Koncepciya profil'nogo obucheniya na starshej stupeni obschego obrazovaniya [Federal Program for the Development of Education; The concept of modernization of Russian education for the period until 2010; The concept of specialized education at the senior level of general education]. (2007, April 26). Retrieved from: http://rudocs.exdat.com/docs/index-387233.html
- Hutchinson, Т., & Waters, A. (1987). English for Specific Purposes: a learning-centred approach. Cambridge, Cambridge University Press.
- Kasprzhak, A. G. (2004). Problema vybora elektivnyh kursov v shkole [The problem of choosing elective courses at school]. Moscow: Novaya shkola.
- Kolesnikov, A. A. (2006). Osobennosti profil'nogo kursa po inostrannym yazykam i ego otlichiya ot bazovyh [Features of a profile course in foreign languages and its differences from basic]. Profilnaya shkola, 3.16-26.
- Konakbeyeva, U., Zholdasbekova, S., & Erdogan, M. (2014). Preparation of future teachers for the organization of profile training in 12-year school. Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences 112, 1232 – 1236.
- Korotkova, M. V. (2007). Dolgij put' idei. Profil'noe istoricheskoe obrazovanie v Rossii [Longwayoftheidea. Profile historical education in Russia]. Pervoe sentyabrya, 6, 31-35.
- Kuznetsov, A. A., Pinsky, A. A., Ryzhakov, M. V., & Filatova, L. O. (2004). Professional'no-tehnicheskoe obrazovanie. Otvety na voprosy (dlya obrazovatel'nyh uchrezhdenij) [Vocationaleducation. Answers to questions (for educational institutions)]. Izv. Ros. Akad. Obrazovaniya, 1, 2-11.
- Lentell, H. (1994). Professional development.Open praxis, (1), 29-30.
- Lerner, P. C. (2004). Rol' elektivnyh kursov v specializirovannom obuchenii [The Role of elective courses in specialized training]. Profilnaya shkola, 3, 12-17.
- Milovanova, L. A. (2006). Profil'noe obuchenie na inostrannom yazyke kak faktor razvitiya yazykovoj identichnosti [Profile training in a foreign language as factor of development of the language identity]. Vestnik oblastnogo gosudarstvennogo uchrezhdeniya, 6, 146-152.
- Passov, E. I. (2000). Kommunikativnoe inoyazychnoe obrazovanie. Koncepciya razvitiya identichnosti v dialoge kul'tur [Communicative foreign-language education. The concept of development of identity in dialogue of cultures]. Moscow: Obrazovanie.
- Schukin, A. N. (2004). Obuchenie inostrannym yazykam: teoriya i praktika: posobie dlya prepodavatelej i studentov [Training in foreign languages: Theory and practice: The manual for teachers and students]. Moscow: Filomatis.
- Takhtamysheva, G. C. (2006). Problemy organizacii profil'nogo obucheniya [Problems of the organization of profile training]. Profilnaya shkola. 6, 50-52.
- Vaisburd, M. L. (2000). Differencirovannoe obuchenie v profil'noj shkole inostrannyh yazykов [Differentiated instruction in the foreign language profile school]. Pedagogika, 7, 232-236.
Copyright information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
About this article
Publication Date
15 November 2020
Article Doi
eBook ISBN
978-1-80296-092-1
Publisher
European Publisher
Volume
93
Print ISBN (optional)
-
Edition Number
1st Edition
Pages
1-1195
Subjects
Teacher, teacher training, teaching skills, teaching techniques, special education, children with special needs, computer-aided learning (CAL)
Cite this article as:
Kartashova, V., Aitov, V., Akberdina, T., & Aitova, V. (2020). Future Teacher Preparation For Profile Training In The University Master's Program. In I. Murzina (Ed.), Humanistic Practice in Education in a Postmodern Age, vol 93. European Proceedings of Social and Behavioural Sciences (pp. 501-513). European Publisher. https://doi.org/10.15405/epsbs.2020.11.52

