Abstract
The need for this research starts from our concrete observation that language education in school does not benefit from adequate support. Language development is crucial in early ages. The age of small schooling is branded by a remarkable potential. If it is not activated, the losses are high and the recoveries are partial for all these children. There are no many curriculum resources centered on the development of communication skills and teachers 'objectives are limited to the development of pupils' cognitive skills, and less social ones. The method used in this study was a questionnaire in a survey among teachers with different experience in teaching and speech development therapy. The sample consisted in 122 teachers whose teaching experience ranges between beginners and experienced. The results of the study showed the following conclusions: teachers seem to be dissatisfied with communication with family in the case of children with language difficulties; school-family partnership is poorly represented in many situations. Technology is an appropriate means of helping to remediate some difficulties of speech, but this is not a unique, miraculous solution. This is not a surprising conclusion, considering that Romanian teachers need many resources to use technology at its real potential for language development.
Keywords: Languageteacherstechnology
Introduction
The language disorder, existing at some point in the child's life, calls for the need for early intervention and especially specialized as early as possible. In the absence of such an approach, there is a stagnation and even a regression in the development of the child and the impossibility to cope later with school requirements or even social adaptation. The early approach to language disorders is essential in the development of the child (Tezci, 2009). The main element is the relationship of interdependence between language and other processes and psychic functions through which human personality is built. Thus, even before entering school, the behavior of the child's psycho-emotional system creates a queue about school results. Achieving a school success threshold is indissolubly linked to the level of global development and ability to adapt behavior to school requirements (Toky & Pange, 2010).
Taking into account everything that has been achieved at the level of technological advancement in the field of looping, we are pleased to note that the novelty elements recorded in the information technology field for a decade are impressive (Miller & Robertson, 2011). The continuing concern of IT specialists to provide high quality educational software to those interested is appreciable because IT products represent a necessary way for students and teachers to meet recent needs related to the development of human potential, processing of information and unusual ways to achieve speech therapy.
Attraction to use the computer is orbserving to all students, the interest in any digital device calls for a growing bending to this area. Behavior and their verbal and nonverbal attitudes enjoy the joy they live when they press the keys and get a result on the screen. Even in cases where the didactic task they receive is difficult (learning writing, for example), the motivation strongly supported by affective positive emotions contributes to the mobilization of the volunteer effort in order to accomplish it. It is noticed that digital platforms, in addition to facilitating a wide range of educational activities, help children play an active role in the learning process and overcome some personal limits. And this category of children is part of the first generation of "digital natives". They acquire skills of software users, provided they are adapted and supported in a psycho-pedagogical way.
Logopedic intervention on the development of language in children from primary classes is a complex approach that requires all the psychic and behavioral components of the child based on the complex knowledge of the child both from the perspective of existing difficulties and outstanding capacities and puts into practice at least the following features of this process:
- any child is capable of progress and development
- Every child has a specific style and rhythm of learning and development
- In any context there is a stagnant potential that is a point of support in learning, development. (Massaro & Light, 2004)
The role of teachers in retrieving and resolving language disorders is an essential one, as the model they offer is viewed by students as a starting point in their psychosocial formation and development. The open, positive attitude, a high degree of motivation and interest in the needs of each student in the class represent the key elements for school success. The teaching style combined with digital resources attracts more and attracts attention. The digital programs and platforms used in speech correction and development have many qualities, including interactivity, colorful visual style, the use of characters from stories specific to children's ages (Popovici, Buică, & Velican, 2010).
Problem Statement
The issue addressed in this research refers to language disorders of primary school children and the role of teacher involvement in alleviating these disorders through the use of digital resources. Another aspect that was analyzed was that of teachers' differences in the use of technology according to the experience they have gained.
Purpose of the Study
The main purpose of this study is to analyze the use of technology in the development of language by teachers. The second objective of this research is to identify differences in the use of technology by without experienced and experienced teachers.
Hypotheses
H1. There is a high level use of technology in language development by teachers in Romania.
H2. There are statistically significant differences in the use of technology by experienced teachers and debutants in Romania.
Research Methods
For this study we chose the survey method based on the questionnaire. We built a questionnaire consisting of 20 items with a Lickert scale response from 1 to 5. The built items were validated by applying the Cronbach alpha statistic test to measure their fidelity. The questionnaire aimed to identify the degree of openness and applicability of technology in the development of language in primary school children by teachers.
Subjects
The participants selected for this study were 122 teachers, with an experience in education between 1-3 years old and experienced over 10 years, all the elected participants have higher education and work in schools in the urban area.All the subjects were randomly selected. The participants were briefly instructed before applying and filling in the three questionnaires.
Findings
The collected data were entered into SPSS statistical software. Due to the normal distribution of data, we were able to apply the
Table
Table
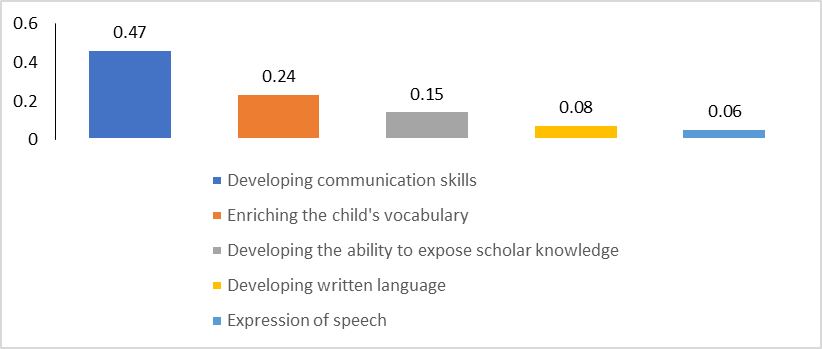
In communication, pupils need to understand their structure and unity, motivate the relationships between the related events, explain them, compare them, discover their common elements, generalize them and draw conclusions. These are some activities designed at the subject called Communication in Romanian Language (CRL), whose most significant goals are related to:
developing communication skills – 47%
enriching the child's vocabulary – 24%
developing the ability to expose scholar knowledge -15%
developing written language – 8%
expressivity of speech – 6 %
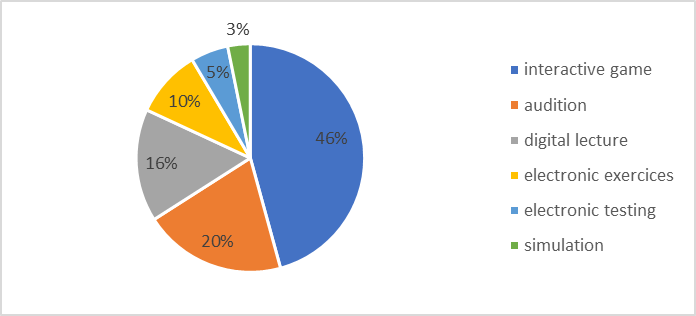
The questioned teachers were asked to give an example of an efficient virtual method for language development. As we see below (see figure 16), next methods have a various choice: interactive games (46%); audition (20%); digital lecture (16%); electronic exercises (10%); electronic testing (5%); virtual simulation (3%).
Conclusions
Therefore, taking into account the results obtained from the research carried out, we can draw the following conclusions: digital resources are an essential tool for making teaching teachers more effective in the educational act and for alleviating students' language disorders. Teachers who have more experience in teaching have more openness to using digital resources, which offers more confidence in the process of integrating and improving students' language problems. Teachers can greatly contribute to correcting these language disorders, student pronunciation, helping them to gain a greater degree of self-confidence, and easier integration and adaptation to classroom staff. Technology is an appropriate means of helping to remediate some difficulties of speech, this is a miraculous solution. The option for digital resources is at a strong level. This is a surprising conclusion, considering that Romanian teachers need many resources to use technology at its real potential. At this moment, there is a lack of resources.
References
- Massaro, D. W., & Light, J. (2004). Using Visible Speech to Train Perception and Production of Speech for Individuals With Hearing Loss, Journal of Speech, Language, and Hearing Research. 47, 304-320.
- Miller D.J., & Robertson, D.P. (2011). Educational benefits of using game consoles in a primary classroom: A randomized controlled trial. British Journal of Educational Technology, 42(5), 850-864
- Popovici, D. V., Buică, C. B., &Velican, V. (2010). Intelligent systems for the diagnosis and therapy of speech-language disorders. Romanian Journal of Experimental Applied Psychology, 1, 60-61.
- Tezci, E. (2009). Teachers’ effect on ICT use in education: the Turkey sample. Procedia Social and Behavioral Science, 157(1), 1285-1294.
- Toky, E., & Pange, J. (2010). E-learning activities for articulation in speech language therapy and learning for preschool children. Procedia Social and Behavioral Sciences, 157(2), 4274–4278.
Copyright information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
About this article
Publication Date
09 April 2019
Article Doi
eBook ISBN
978-1-80296-059-4
Publisher
Future Academy
Volume
60
Print ISBN (optional)
-
Edition Number
1st Edition
Pages
1-1062
Subjects
Multicultural education, education, personal health, public health, social discrimination,social inequality
Cite this article as:
Pânișoară, G., Sandu, C., Făt, S., & Lazăr, I. (2019). Study On The Use Of Technology In Language Development By Teachers. In E. Soriano, C. Sleeter, M. Antonia Casanova, R. M. Zapata, & V. C. Cala (Eds.), The Value of Education and Health for a Global, Transcultural World, vol 60. European Proceedings of Social and Behavioural Sciences (pp. 841-846). Future Academy. https://doi.org/10.15405/epsbs.2019.04.02.104

