Abstract
The concept of risk-based approach to economic security is able to focus its consideration of individual goals in interdependent groups, that is, where there is a cross functional of different centers responsible for economic security. Ensuring a reliable reporting system and law observance are in the responsibility of the economic entity, and it is able to influence on these processes. A properly formulated approach to risk management can guarantee the achievement of objectives. This study reveals the main categories included in the concept of risk-oriented approach and the relevance of its implementation in the system of economic security of business entities. Particular attention is paid to the strategic component of the risk-oriented model of economic security of the enterprise: its key components and components of the risk management process, reflecting the relationship between the strategic planning and risk-oriented approach within the framework of this system. The authors conducted a graphical study of the risk areas of an economic entity, conducted modeling of risk-free situations and demonstrated their graphical representation. At the same time, the areas of acceptable risk are modeled taking into account the requirements of key stakeholders of economic entities – shareholders. On the example of a commercial enterprise risks as the main component of the risk-oriented system of economic security has been highlighted.
Keywords: Economicsecurityrisk-orientedapproacheconomic entityriskrisk managementstrategic planning
Introduction
According to some scientists, economic security is a characteristic of economic entity that contributes, first of all, to its protection from the influence of external and internal negative factors. The opposition to the negative impact in the framework of economic security actualizes the need to consider the risks of activity as the probability of negative consequences.
Risk-oriented approach conception
The risk-oriented approach involves the formation of the enterprise strategy as a whole, and business processes in particular, which, on the one hand, is able to warn about the emergence of risks, and, on the other, to minimize the negative impact of them on the activities of the economic entity. That is why the concept of risk orientation has recently been recognized by many researchers as more promising in relation to the practical aspect of business functioning than the concept of sustainable development (Thompson & Strickland, 2002). Thus, the proponents of this position cite as an argument a high level of uncertainty in economic relations, as well as a high degree of influence of political factors that prevent the formation of prerequisites for sustainable development, while systematic measures aimed at identifying risk and minimizing its negative impact are most applicable in the new normality (Belorusova & Rezkin, 2013).
Moreover, the risk-orientation of the business model also seems to be an effective method of overcoming not only private risks, but also large-scale, conjunctural changes that appear due to the cyclical nature of economic processes (Kiseleva, 2017). Early detection, prevention or minimization of the consequences of risk can also be considered as a key tool for managing the life cycle of the organization, when management is able to make management decisions that extend the favourable stages of the business.
The importance of risk-oriented approach in the system of enterprise economic security
Systematic actions for risk preventing or minimizing its negative consequences are necessary in order to ensure the economic security of the economic entity. Despite the high development of the modern methodology of the organization state forecasting procedure, the possibility of automating the calculation of key indicators and the compilation of econometric models, is still not possible to obtain an accurate forecast of the values of risk indicators and its consequences (Petersen, 2013). Therefore, in practice, the foresight method is widely used. Foresight is a simulation of scenarios of the situation in the context of various combinations of parameters and factors and the development of appropriate measures for each scenario to prevent risk or minimize its negative consequences (Raišienė, 2012).
Problem Statement
Particular importance in the formation of a reliable system of economic security should be given to the development of a strategic plan of the economic entity (Senchagov, 2015). The focus on risk, both in the management of the enterprise as a whole and its economic security in particular, should not be included in the framework of a reactive model of managerial decision-making, implying the constant preparation of decisions aimed to overcome emerging problems (Burtsev & Romanchenko, 2017). On the contrary, the risk orientation of the enterprise economic security system is one of the conditions that guarantee the full formation of the conditions necessary for the implementation of the enterprise strategy.
Strategic planning in the system of enterprise economic security
Achieving the objectives of strategic planning largely depends on the mechanism of economic security in the static and dynamic manifestation, with economic and legal positions. The key components of the strategic plan are shown in figure
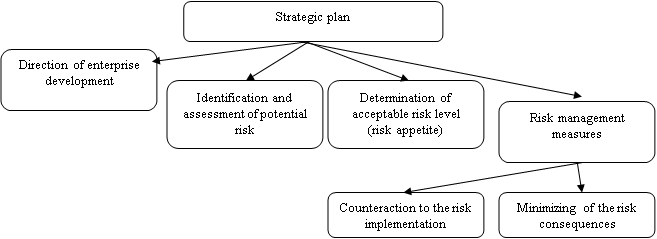
As part of the formation of the strategic plan, the study of parameters and indicators characterizing the state of financial and economic activity of the economic entity is carried out, techniques and methods of influencing the totality of internal and external factors from the standpoint of strengthening economic security are developed, critical values are determined, or a corridor of values of indicators beyond which signals the emergence of threats, and a plan of measures to respond to emerging risks is drawn up (Widener, 2007).
Risk management in the system of enterprise economic security
At the same time, the achievement of strategic business goals should be based on activities that would be able not only to minimize the risks of the enterprise economic security, but also fully contribute to the realization of the advantages of assortment, price, credit, financial policies of the organization, and other competitive advantages of the company.
The practical implementation of a risk-based approach to economic security is a search for the most relevant risks for a particular business from the whole range of possible threats (Glotova & Tomilina, 2016). The process of developing the concept of risk management in the selected areas is based on the conceptual foundations of the theory of restrictions Goldratt, implying a continuous search for the most relevant risks in order to develop measures to counter them (Goldratt, 1998).
As an alternative approach to the position of risk minimization, a number of economists consider the optimization of risk achieved through a series of consistent actions that allow a balance of risk and profitability. Risk management from the position of its optimization can be described using the following algorithm, shown in figure
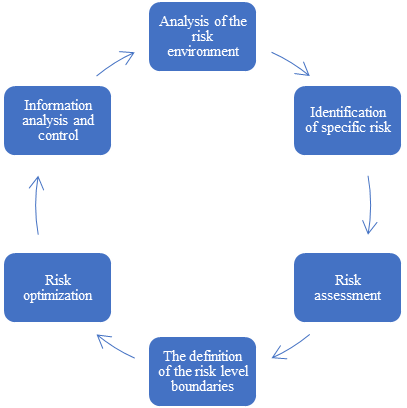
Also, in the context of economic security in the framework of strategic planning, the following areas of risk management are developed (table
The beginning of the risk management process is a determine of the risk appetite level, expressed in the amount of money that the entity is ready to lose when implementing risk in conditions of low efficiency of measures to minimize it.
Research Questions
Within this study the following research questions were highlighted:
What is the essence of risk-oriented approach in the system of enterprise economic security?
What is the importance of strategic planning in the risk-oriented system of enterprise economic security?
What is a map of risk areas as a risk management tool within the economic security system of the enterprise?
Purpose of the Study
Within the study, the following goals were set:
To investigate the essence of risk-oriented approach and strategic planning in the system of enterprise economic security, to reveal their interrelation;
To identify the algorithm, directions and components of risk management in the the enterprise economic security;
To reveal the design of risk maps, using graphical method.
Research Methods
A risk-based approach to economic security affects all activities of the organization and requires the involvement of a wide range of staff, from shareholders and senior management, to ordinary employees who have direct interaction with the sources of potential risks. In addition, it is advisable to detail the risk-orientation program and adapt it to the activities of each structural unit or business process.
Another parameter necessary for strategic planning within the risk-oriented approach to economic security is risk appetite, which reflects the size and types of uncertainty acceptable to the organization in the course of achieving its goals (Radukov & Kolesnichenko, 2016). As a rule, the acceptable level of risk, should be expressed in units of measurement corresponding to the strategic goals, and represents an acceptable level of deviation from the goal (Sopko & Stetsenko, 2014). At the same time, it is possible to form a balanced approach to the definition of risk appetite, if necessary, taking into account the priority of strategic goals and identified risks.
Characteristics of the quantitative aspect of the risk appetite indicator
Quantitative assessment of risk appetite indicator is possible in two ways:
1. Top-down - acceptable risk is considered as a share of profit before tax or capital;
2. Down-top - a retrospective analysis of costs and expenses, as well as studies of financial condition.
Thus, the methodological basis of the quantitative expression of the economic entity risk appetite is actively replenished today due to the increased practical and scientific interest in this issue (Menggang, 2013). In particular, it presents and substantiates the ways of calculating the indicator of risk appetite as using multi-factor models, and defined by experts, or regulated by the management decisions.
However, from the author's point of view, the approach to the calculation of risk appetite as a ratio of financial strength to revenue requires attention. The advantages of this indicator are:
1. Compliance with current financial and economic activities. Any change in costs, regardless of their variable or constant nature, will affect the break-even point, which will have an impact on the amount of financial safety margin.
2. Availability of information base for calculation of indicators. The calculation of this indicator is based on accounting parameters and does not require additional costs for the formation of an information base;
3. High analyticity of the indicator. This indicator not only determines the scale of risk appetite in the area of risks that can lead to a reduction in the potential income of the organization, but also the risks of production and organizational and managerial nature, determined by variable and fixed costs (D'Agostino, 2008).
The relationship of strategic planning and risk-oriented approach in the system of enterprise economic security
Within the strategic planning, the formed mission of the organization determines strategic and tactical goals. In this case, special attention should be paid to the area of reporting and compliance with the legal framework of doing business (Mullakhmetov, Aminova, & Akhmetshin, 2014). Systematization of strategic and tactical goals provides an opportunity to assess the expected results and risks differentially.
Strategic and tactical (operational) goals, as a rule, are directly related to external events, therefore, the process of obtaining reliable information about the degree of achievement of strategic business goals becomes extremely important for the structural units of the organization performing the supervisory function.
The relationship between strategic, tactical, reporting and compliance objectives and risk management components reflects the organization's ability to consider risk management in the economic security system in its entirety and across all categories of objectives, depending on the scale of management.
In the basis of risk management there are interrelated components that are part of the management process, the content of which is determined by the management decisions of the economic entity.
The components of the risk management process are presented in table
The presence of management components and the degree of their functioning, reducing the risk to the limits that do not go beyond the quantitative determination of the risk appetite of the company, can become criteria for the effectiveness of risk management. The use of these components in each company is individual and reflects the specifics of the business. For example, in small and medium-sized businesses, this process is less formalized and structured, due to the lack of qualified personnel and financial resources necessary for the system operation.
Depending on the size of the losses, a number of economists distinguish the risk zones presented in table
This approach illustrates the definition of risk zones in accordance with the probability of their realization and the amount of possible losses. The information basis for calculating the amount of possible losses is the accounting (financial) statements of the organization.
Findings
The relationship between the size of losses and the probability of the risk realization is expressed in the map of risk areas. It shows how likely losses are to occur, forming a complete picture of the risk, which allows us to assess its acceptability to the organization.
A graphical representation of the risk areas is shown in figure
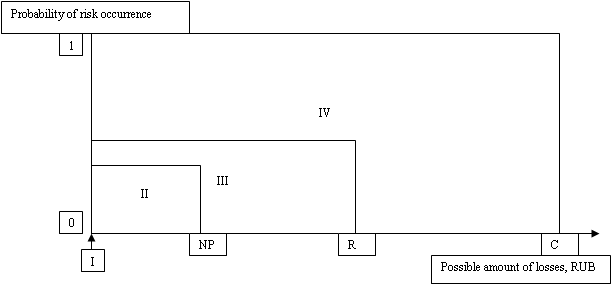
Note:
NP - possible losses equal to the amount of the organization's net profit;
R - the possible amount of losses equal to the amount of enterprise revenue;
C - the possible amount of losses equal to the amount of enterprise capital.
Riskzones: I - Risk-freezone; II - Zone of acceptable risk; III - Zone of critical risk; IV - Zone of catastrophic risk.
This method allows to detail risk areas, introducing additional boundaries. It is possible to detail the area of permissible risk in the area of compliance with the interests of shareholders and non-compliance with the interests of shareholders, where the border on the abscissa axis will serve as an indicator equal to the amount of dividends planned for payment. It is also possible to detail the zone of acceptable risk to the area of acceptable risk without threats to development and the area of acceptable risk with a threat to development, where the border will serve as a value equal to the part of the net profit that is planned to be directed to R&D(research and development) and innovation (Anisimov, Zhuravlev, & Kuksova, 2015). Suppose that according to the shareholders decision, the amount allocated for the payment of dividends exceeds the planned investment in R&D. In this case, the proposed areas will look as shown in figure
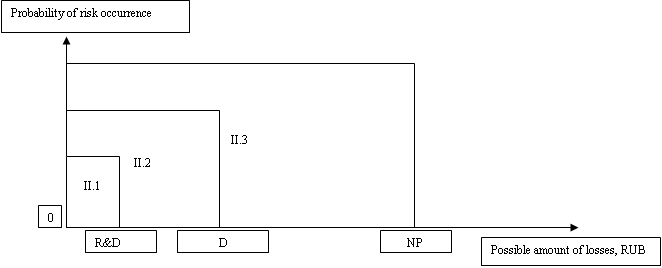
Note:
NP - possible losses equal to the amount of the organization's net profit;
D - possible amount of losses equal to the amount of funds planned for dividend payment;
R&D - possible amount of losses equal to the amount of funds planned for R&D financing зарассматриваемыйпериод;
Области:
II.1 - the area of acceptable risk without threat to development and in compliance with the interests of shareholders;
II.2 - the area of acceptable risk with a threat to development and in compliance with the interests of shareholders;
II.3 - the area of acceptable risk with a threat to development and without compliance with the interests of shareholders.
The identification of risks that determine the level of enterprise economic security, as well as the development and implementation of risk management procedures is preceded by the analysis of risk assessment methodologies and the development of own, individual for each organization methodology (Dawnay & Hetan, 2005). To assess the level of relevance of the consequences of the onset of trade risks of the organization, as the most significant to the Russia realities identified in the analysis of financial and economic activities, it is advisable to apply the methodology recommended by the Institute of internal auditors (IIA), which allows at the stage of management decisions on the basis of retrospective analysis of reporting data to classify risks by ranges: acceptable level of risk (within the risk appetite), critical and catastrophic.
Thus, for the risks that fall within the range of the catastrophic level, representing the greatest threat to the stable operation of the enterprise, solutions that can minimize the risk will be recommended, as well as the effectiveness of the proposed measures will be evaluated.
Taking into account the peculiarities of the internal and external environment, as well as the development of a number of economists covering this topic, the following risks were identified, the most inherent activities of Russia trade enterprises:
1. Risk of unclaimed goods;
2. Risk of theft;
3. The risk of the unreliability of the debtor;
4. Risk of the goods for resale delivery schedule violation;
5. Risk of over-lending;
6. The risk of insufficiency of own funds to cover liabilities;
7. The risk associated with the supplier's monopoly.
On the allocated risks it is possible to designate the centers, the reasons and consequences of emergence risk.
Conclusion
The introduction of a risk-oriented approach to economic security is a very time-consuming process. However, the possible economic benefits of its implementation can exceed the costs incurred for its organization. If the principle of economic expediency is observed, the introduction of this system in the enterprise can be justified.
In addition, the risk management process at the enterprise is complicated by the fact that the results of analytical work, on the basis of which management decisions are made, can be erroneous and do not correspond to modern business realities. So, the decision to apply a particular method of risk and ensuring adequate controls may not consider the balance of costs and the result to contain the error received in the power of human factor in control procedures may not be implemented because of deliberate collusion or intentional violations of internal security procedures, which leads to a lower likelihood of achieving strategic goals.
Identification of risks by the organization is provided by drawing up the list of risk sources which defines potential risk zones, is performed concerning all operations, including the operations demanding application of professional judgment in the absence of exact methods and methods of calculation of estimated values, methods of recognition of the income, expenses or demanding assumptions about influence of future uncertain events.
References
- Anisimov, I. V., Zhuravlev, Yu. V., & Kuksova, I. V. (2015). The role of innovative potential in the management system of enterprises economic security. Bulletin of Voronezh State University of engineering technologies, 2, 243-247.
- Belorusova, N. L., & Raskin, P. E. (2013). The concept of an integrated accounting information system of enterprise economic security. Bulletin of Polotsk State University. Series D, Economic and legal Sciences: scientific and theoretical journal, 6, 30-34.
- Burtsev, Yu. A., & Romanchenko, L. N. (2017). The process of ensuring the enterprise economic security. Successes of modern science and education, 4, 72-75.
- D’Agostino, D. (2008). Defense Critical Infrastructure: Risk Analysis of Critical Infrastructure Omits Highly Sensitive Assets. Washington: US Gout Accountability Office.
- Dawnay, E., & Hetan, S. (2005). Behavioural Economics: seven principles forpolicy-makers. New Economic Foundation, London, July.
- Glotova, I. I., & Tomilina, E. P. (2016). Threats to the economic security and the direction of neutralization in the system of economic security of enterprise. Economic security: legal, economic, and ecological aspects,2. 29-33.
- Goldratt, E.M. (1998). Late Night Discussions on the Theory of Constraints. ISBN 0-88427-160-9
- Kiseleva, I. A. (2017) Economic security of the enterprise. Business. Education. Right, 4 (41), 33-37.
- Menggang, L. (2013). Research on industrial security theory. Springer Berlin Heidelberg, 443.
- Mullakhmetov, K. S., Aminova, R. M., & Akhmetshin, E. M. (2014). Control in a management system in modernconditions. Asian Social Science, 10 (24), 237-247.
- Petersen, K. (2013). The Corporate Security Professional: A hybrid agent between corporate and national security. Security Journal, 26, 222-235.
- Radukov, Y. Y., & Kolesnichenko, E. A. (2016). Technique of estimation of economic security level in the economic subsystem in terms of the impact of external determinants. Region: systems, Economics, management, 2, 79-86.
- Raišienė, A. G. (2012). Sustainable development of interorganizational relationships and social innovations. Journal of Security and Sustainability Issues, 2 (1), 65–76.
- Senchagov, V.S. (2015). The economic security of Russia. General Course. Moscow: Publishing House BEAN Laboratory of Knowledge, 816.
- Sopko, V.V., & Stetsenko, I. V. (2014). Problems of analysis of economic security of the enterprise. Economics and management: analysis of trends and prospects, 16, 89-96.
- Thompson, A. A., & Strickland, A. J. (2002). Strategic Management: Concepts and Cases. Moscow: Williams publishing house, twelfth edition, 928
- Widener, S. (2007), An empirical analysis of the levers of control framework. Accounting, Organizations and Society, 32, 757-788.
Copyright information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
About this article
Publication Date
20 March 2019
Article Doi
eBook ISBN
978-1-80296-056-3
Publisher
Future Academy
Volume
57
Print ISBN (optional)
-
Edition Number
1st Edition
Pages
1-1887
Subjects
Business, business ethics, social responsibility, innovation, ethical issues, scientific developments, technological developments
Cite this article as:
Kalashnikova, E., Tatarovskaya, T., & Tselniker, G. (2019). Risk-Oriented Approach In The System Of Enterprise Economic Security. In V. Mantulenko (Ed.), Global Challenges and Prospects of the Modern Economic Development, vol 57. European Proceedings of Social and Behavioural Sciences (pp. 677-687). Future Academy. https://doi.org/10.15405/epsbs.2019.03.67

