Abstract
This study identifies the factors that affecting the financial performance of Takaful operators in Malaysia. Data were gathered using secondary data collection method from annual report for each of Takaful operators and Bank Negara Malaysia from year 2007 until 2016. The data consist of profitability, leverage, liquidity and firm size for 5 registered Takaful operators in Malaysia namely; Syarikat Takaful Malaysia Berhad, Takaful Ikhlas Sdn Bhd, Prudential BSN Malaysia Berhad, Sun Life Malaysia Takaful Berhad (CIMB Aviva Takaful Berhad) and Hong Leong MSIG Takaful Berhad. Data were analysed using multiple regression analysis. From the analysis, firm size was found significantly positive effect towards financial performance. In contrast, leverage and liquidity were found significantly negative effect related to the financial performance. Thus, this study is very important and beneficial to regulators, investors and customers. As recommendation, Takaful operators should improve their sales in order to enhance the consistency of profit growth. Besides that, Takaful operators need to disclose the financial report from the beginning because it could make an easier for researcher in collecting data. Moreover, as the Islamic insurance that applies
Keywords: Takaful operatorsfinancial performanceleverageliquidityfirm size
Introduction
Takaful or Islamic insurance is coined from the Islamic word kafalah, which means ‘guaranteeing each other’ or ‘joint guarantee’. This concept which is grounded in Islamic Muamalat, observing the rules and regulation of Islamic law that involves participants and operators. Participants will contribute a certain amount to a fund as his or her obligation and managed by a third party which is called Takaful operators as a protection and profit sharing venture. Takaful operators will disburse the funds accordingly to its participants when the event of loss or damage suffered. In Malaysia, there are 11 registered Takaful operators which included 2 foreign and 9 local Takaful operators. According to statistics by Bank Negara Malaysia (BNM), Takaful operators have been showing rising from the year 2010 until 2015. It is supported by Fitch Ratings report, where Malaysian Takaful sector saw strong growth in 2015. Besides that, BNM also reported Malaysia dominates two-third market share of Takaful in ASEAN.
Financial Performance
Financial performance is an essential to management as the act of performing the financial activity. It can be used to compare with similar companies across the same sectors to measure overall financial health at a certain period. Hidayat and Firmansyah (2017) stated that assessing the financial performance of companies can be measured by Return on Assets (ROA) which focuses the company’s ability to earn profit from its assets. Based on the study done by Siminica
Leverage
Chen and Wong (2004) claims that leverage beyond the optimum level could result in higher risk and low value of the firm. According to Almajali
Liquidity
A company can use liquid asset to finance its activities and investment if inaccessibility from external financing. According to Shiu (2004), a company will perform better and less expose to liquidity risk if the company’s asset is more liquid. It is because they are able to realize cash at any time to meet its obligations. On the other hand, study done by Arshad
Firm Size
Sambasivam and Ayele (2013) found that firm size was statistically significant and positive relationship towards financial performance. Firm size is used to release the fact that larger insurance companies are better positioned than smaller once in harnessing economies of scale in transactions and adore a higher level of profits. Based on the empirical result, size of the company is statistically significant towards the performance of the general Takaful in Malaysia. Hidayat and Firmansyah (2017), Almajali
Problem Statement
Financial performance is a primary concern in all types of industry including with Takaful industry. Financial performance is an indicator for organization’s well-being and ultimately its subsistence. The good financial performance reflects the management effectiveness and competence in using the company resources. Takaful Ikhlas annual report has recorded progressive growth during the period of 2009 until 2016 as shown in Figure
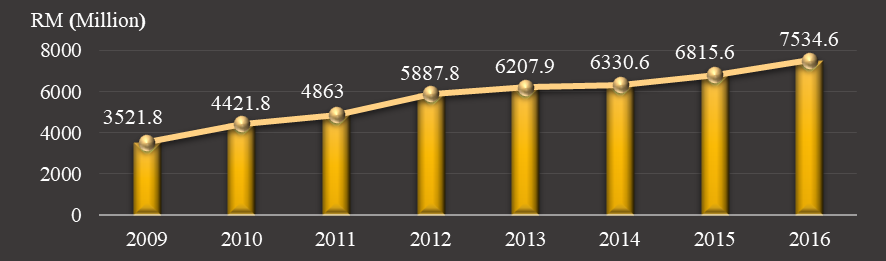
A study done by Almajali
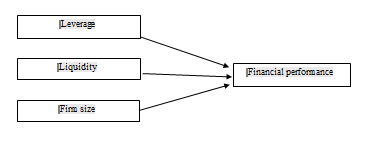
In addition to that, there are a lot of researches focused on determinants factors that affecting the financial performance of banks rather than insurance companies especially in Malaysia. Thus, this study is very important and beneficial to regulators, investors and customers. By understanding determinants contributing to the financial performance, the regulators could play a vital role in helping Takaful operators to increase their market share. For investors, they can choose their investment places while customers will select the best Takaful operators for their Islamic insurance protection. Hence, this study used ROA to measure financial performance as dependent variable, whereas leverage, liquidity and firm size as the independent variables, in identifying the factors that affecting the financial performance of Takaful operators in Malaysia.
Research Questions
Is there any significant effect of leverage, liquidity and firm size towards financial performance of Takaful operators in Malaysia?
Purpose of the Study
To identify the factors that affecting the financial performance of Takaful operators in Malaysia.
Research Methods
Data for this study were obtained using secondary data collection method. The data consist of profitability, leverage, liquidity and firm size for 5 registered Takaful operators in Malaysia namely; Syarikat Takaful Malaysia Berhad, Takaful Ikhlas Sdn Bhd, Prudential BSN Malaysia Berhad, Sun Life Malaysia Takaful Berhad (CIMB Aviva Takaful Berhad) and Hong Leong MSIG Takaful Berhad. A total of 11 registered Takaful operators but only 5 Takaful operators were selected because the limitation of data. The data were collected from annual report for each of Takaful operators and Bank Negara Malaysia from year 2007 until 2016.
Regression model
This study used multiple regression analysis to test the effects of leverage, liquidity and firm size on financial performance of Takaful operators in Malaysia. The regression models used in this study are as the following:
Where:
FP = financial performance; α = constant value; β = regression coefficient; LV = leverage; LQ = liquidity; FS = firm size; and ε = residual term
Based on the preceding discussion, five hypotheses are developed:
H1: There is a significant effect of leverage towards financial performance of Takaful operators in Malaysia.
H2: There is a significant effect of liquidity towards financial performance of Takaful operators in Malaysia.
H3: There is a significant of firm size towards financial performance of Takaful operators in Malaysia.
Findings
Table
On the other hand, leverage (
In addition,
Last but not least, Variance Inflation Factor (VIF) test is to avoid bias decision making process that will affect a part of independent variables on the dependent variable. Based on the table
Conclusion
The main purpose of this study has been answered where all the independent variables, leverage, liquidity and firm size are affected to the Takaful operator’s financial performance. From the findings, firm size has significantly positive effect related to financial performance. The positive effect between financial performance and firm size are consistent with prior studies by Hidayat and Firmansyah (2017), Sambasivam and Ayele (2013), Almajali
However, leverage and liquidity have significantly negative effect towards financial performance of Takaful operators in Malaysia. For leverage, the result was consistent with the study done by Hidayat and Firmansyah (2017), Sambasivam and Ayele (2013) and Malik (2011). The finding suggested that high leverage will lead to the high risk of company’s bankruptcy if they are unable to pay their debt obligations. Reducing debt of the company shows the more effective the company managing their debt. On the other hand, the result for liquidity was supported by Sambasivam and Ayele (2013). Higher liquidity of the Takaful operators will lead them managing their asset very well. Liquidity is one of the instruments that measure how quickly the company convert their assets into cash. As conclusion, the finding of this study can be used to contribute towards a better understanding about the financial performance of Takaful operators in Malaysia.
As recommendation, Takaful operators should improve their sales in order to enhance the consistency of profit growth. Nowadays, the developments of Malaysia Takaful operators become the world attention. Therefore, the improvement of sales is very important. Besides that, Takaful operators need to disclose the financial report from the beginning because it could make an easier for researcher in collecting data. Moreover, as the Islamic insurance that applies
Limitations and future research
There is obvious limitation while conducting this study in terms of data collection. In Malaysia, we have 11 registered Takaful operators, however, this study only used 5 Takaful operators due to limited accessibility in collecting the data. In addition, these 5 Takaful operators were among the earliest local operators that registered in Bank Negara Malaysia. Thus, this study would be an indicator to the other Takaful operators in sustaining their performance.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the anonymous reviewers who will give their extensive and thorough comments which had enormously helped us improved the quality of our paper. The perspectives and the positioning of our paper has certainly benefited from their valuable feedback and comments.
References
- Ali, M. (2014). Relationship between financial leverage and financial performance (evidence of listed chemical companies of Pakistan).. Research Journal of Finance and Accounting,, 44(23), 2222-2847
- Almajali, A Y.Alamro, S A.Al-Soub, Y Z. (2012). Factors affecting the financial performance of Jordanian insurance companies listed at Amman Stock Exchange.. Journal of Management Research,, 44(2), 266-
- Arshad, Z.Gondal, M Y.Hussain, T. (2016). Factor affecting the Financial Performance of Takaful Companies in Pakistan.. Asian Journal of Research in Banking and Finance,, 44(1), 14-21
- Chen, R.Wong, K A. (2004). The determinants of financial health of Asian insurance companies.. Journal of Risk and Insurance,, 44(3), 469-499
- Gujarati, D N. (2003). Basic Econometric 4th Edition.
- Hardwick, P.Adams, M. (1999). The determinants of financial derivatives use in the United Kingdom life insurance industry.. Abacus,, 44(2), 163-184
- Hidayat, I P.Firmansyah, I. (2017). Determinants of Financial Performance in the Indonesian Islamic Insurance Industry.. Etikonomi,, 44(1)
- Hong Leong MSIG Takaful Berhad, (). Hong Leong MSIG Takaful Berhad. The annual report , retrieved from https://www.hlmtakaful.com.my
- Key financial indicators Islamic banking and Takaful sectors., (2016). Key financial indicators Islamic banking and Takaful sectors., Retrieved from http://www.bnm.gov.my.
- Fitch, . (2016, January 05). Malaysian Takaful sees increasing systematic importance., Retrieved from https://www.fitchratings.com
- Ismail, M. (2013). Determinants of financial performance: The case of general takaful and insurance companies in Malaysia.. International Review of Business Research Papers,, 44(6), 111-130
- Liargovas, P G.Skandalis, K S. (2010). Factors affecting firms’ performance: The case of Greece.. Global Business and Management Research: An International Journal,, 44(2), 184-197
- Malik, H. (2011). Determinants of insurance companies’ profitability: An analysis of insurance sector of Pakistan.. Academic Research International,, 44(3), 315-
- Prudential BSN Berhad, (). Prudential BSN Berhad. The annual report , retrieved from https://www.prubsn.com.my
- Sambasivam, Y.Ayele, A G. (2013). A study on the performance of insurance companies in Ethiopia.. International Journal of Marketing, Financial Services & Management Research,, 44(7), 138-150
- Shiu, Y. (2004). Determinants of United Kingdom general insurance company performance.. British Actuarial Journal,, 44(5), 1079-1110
- Siminica, M.Circiumaru, D.Simion, D. (2012). The correlation between the return on assets and the measures of financial balance for Romanian companies.. International Journal of Mathematical Models and Methods in Applied Sciences,, 44(1), 249-256
- Sun Life Malaysia Takaful Berhad, (). Sun Life Malaysia Takaful Berhad. The annual report , retrieved from https://www.sunlifemalaysia.com
- Syarikat Takaful Malaysia Berhad, (). Syarikat Takaful Malaysia Berhad. The annual report , retrieved from https://www.takafulmalaysia.com.my
- Takaful Ikhlas Sdn, (). Takaful Ikhlas Sdn. Bhd. The annual report , retrieved from https://www.takaful-ikhlas.com.my
- Takaful industry likely to sustain double-digit growth in 2016, 2017., (2016, November 17). Takaful industry likely to sustain double-digit growth in, Retrieved from http://web10.bernama.com
Copyright information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
About this article
Publication Date
31 July 2018
Article Doi
eBook ISBN
978-1-80296-043-3
Publisher
Future Academy
Volume
44
Print ISBN (optional)
-
Edition Number
1st Edition
Pages
1-989
Subjects
Business, innovation, sustainability, environment, green business, environmental issues, industry, industrial studies
Cite this article as:
Ismail, N., Izam, F. N. N. A., Samsuddin, N. A., Ishak, I., & Manaf, N. A. (2018). Factors Affecting Financial Performance Of Takaful Operators In Malaysia. In N. Nadiah Ahmad, N. Raida Abd Rahman, E. Esa, F. Hanim Abdul Rauf, & W. Farhah (Eds.), Interdisciplinary Sustainability Perspectives: Engaging Enviromental, Cultural, Economic and Social Concerns, vol 44. European Proceedings of Social and Behavioural Sciences (pp. 441-448). Future Academy. https://doi.org/10.15405/epsbs.2018.07.02.47

